Outdoor theater in parks and gardens
Features, functionality, types, and planning
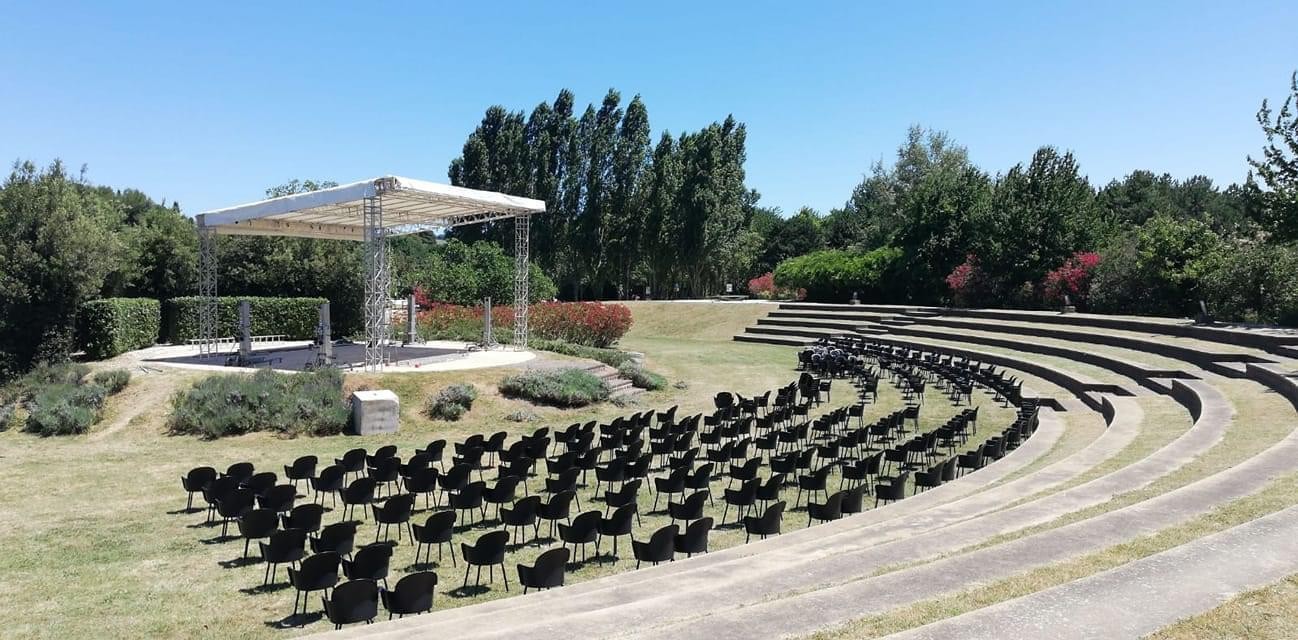

Outdoor theater in urban public parks and gardens is a form of entertainment that combines the art of acting with the beauty of nature. These spaces offer a unique opportunity for artists to perform in the open air, creating a magical and engaging atmosphere for the audience. In this article, we will explore the characteristics of these theaters, their functionality, different types of designs, and considerations for designing an outdoor theater in an urban public park.
Advantages of outdoor theater in urban public parks
Outdoor theater in urban public parks and gardens offers a number of unique benefits for the community and artists. First, these spaces provide an opportunity to enjoy art and culture in a natural and relaxing environment. This contributes to people’s well-being and happiness by offering a break from the hustle and bustle of daily life. In addition, outdoor theater in parks can help create a sense of community and belonging, encouraging people to socialize and share cultural experiences together.
Characteristics and functionality of outdoor theater spaces
Outdoor theaters are characterized by a number of distinctive elements that contribute to their uniqueness and beauty.
- Nature. Outdoor theaters are spaces surrounded by nature, this creates a charming and romantic atmosphere. The surrounding trees, flowers and greenery create a perfect backdrop for theatrical performances.
- Open stage. These theaters often feature an open stage, which allows actors to interact with the audience in a more direct and engaging way. This creates a sense of intimacy and connection between performers and audience members.
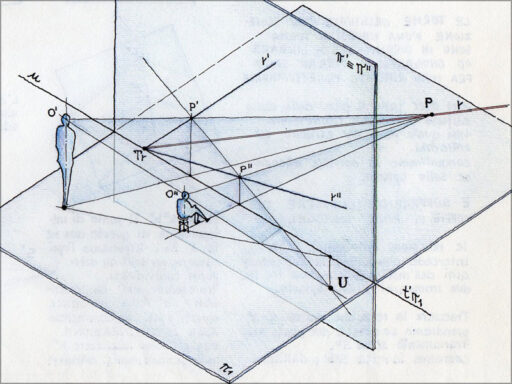
- Light and acoustics. Outdoor theaters are designed to take full advantage of the natural light and acoustics of the venue, providing a unique sensory experience.
Outdoor theater incorporated into urban public parks and gardens is not only a place of entertainment, but also serves a number of important community functions. First, these spaces provide an opportunity for local artists to perform and introduce their talents to the public. In addition, the outdoor theater can be used for cultural events, festivals, and concerts, attracting tourists and visitors to the area. This contributes to the dynamism and vitality of the surrounding area. In addition, the outdoor theater can be a social gathering place, where people come together to enjoy a show together and make connections with other community members.
Different types of outdoor theater projects
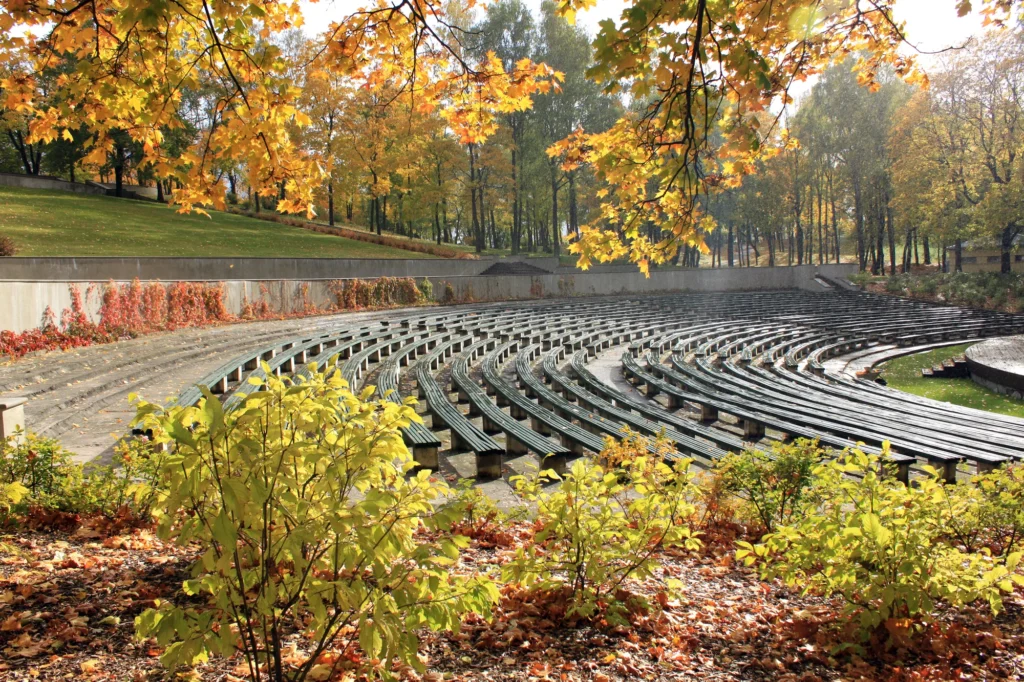
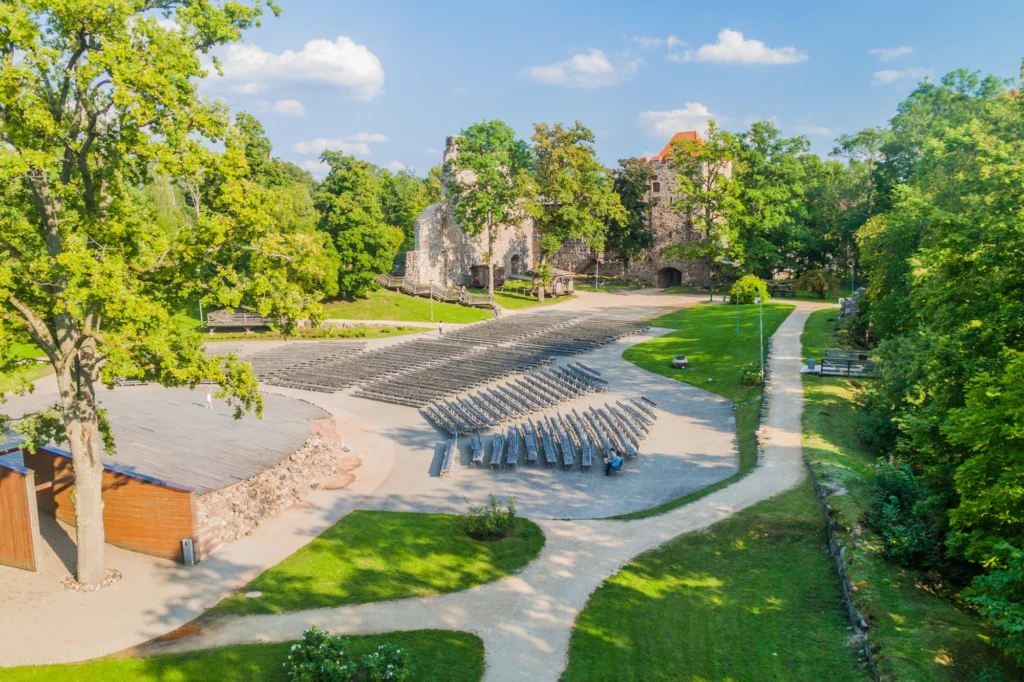
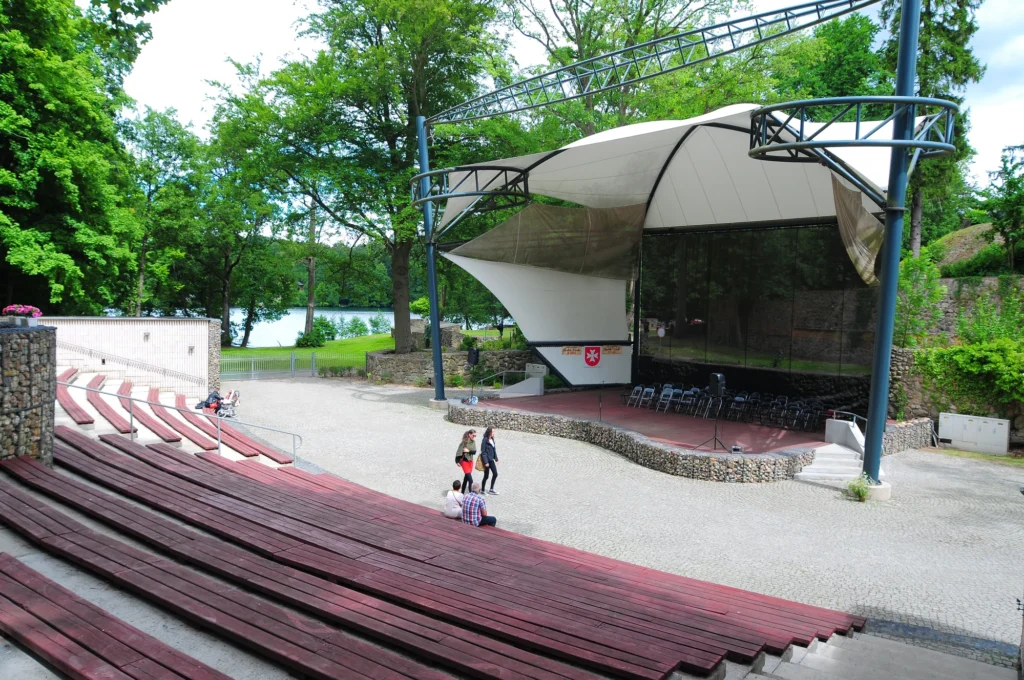
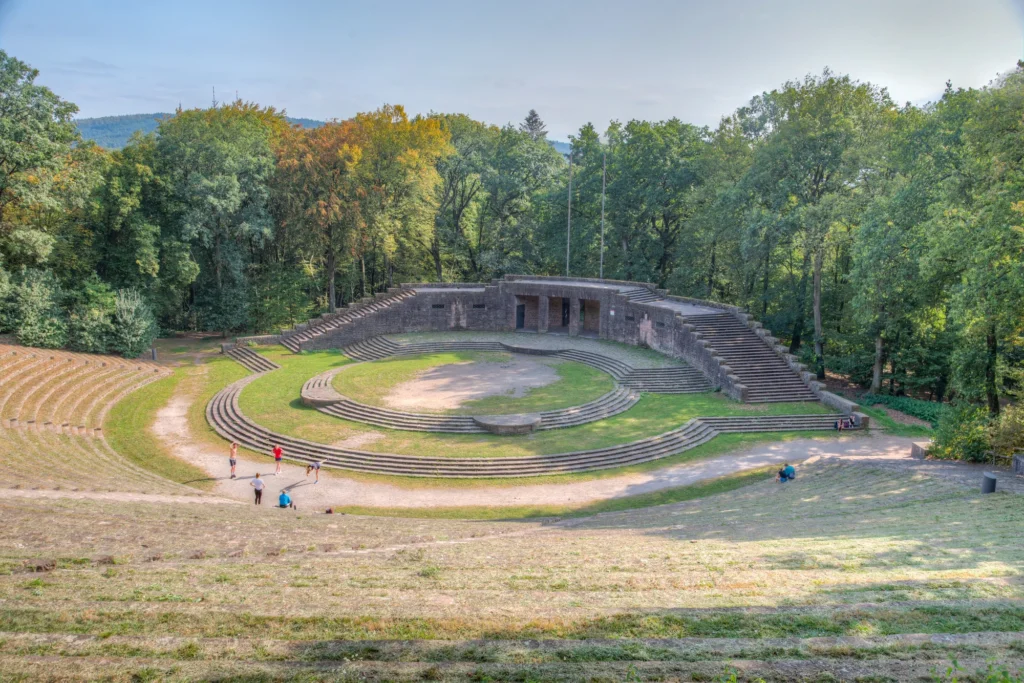
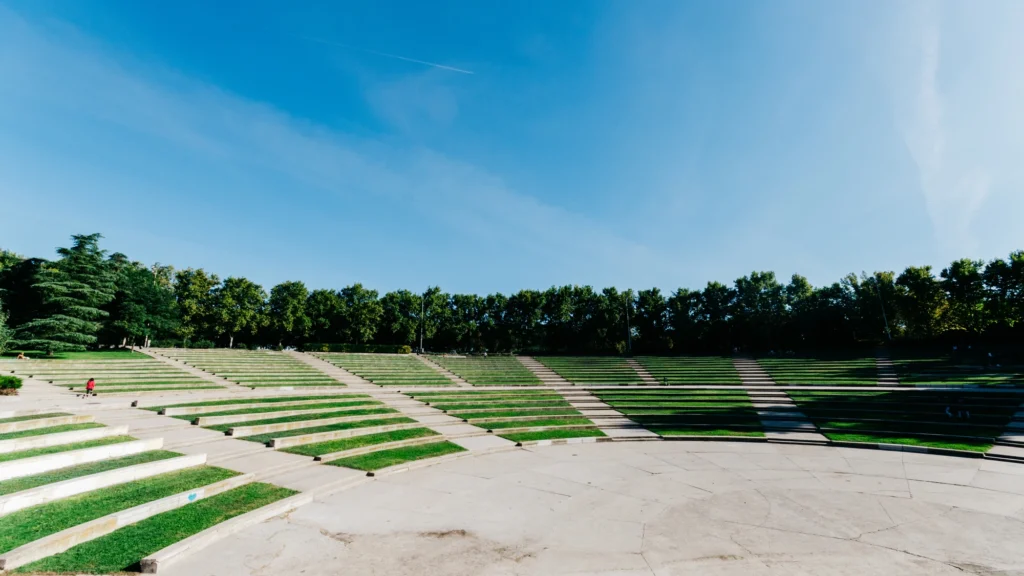
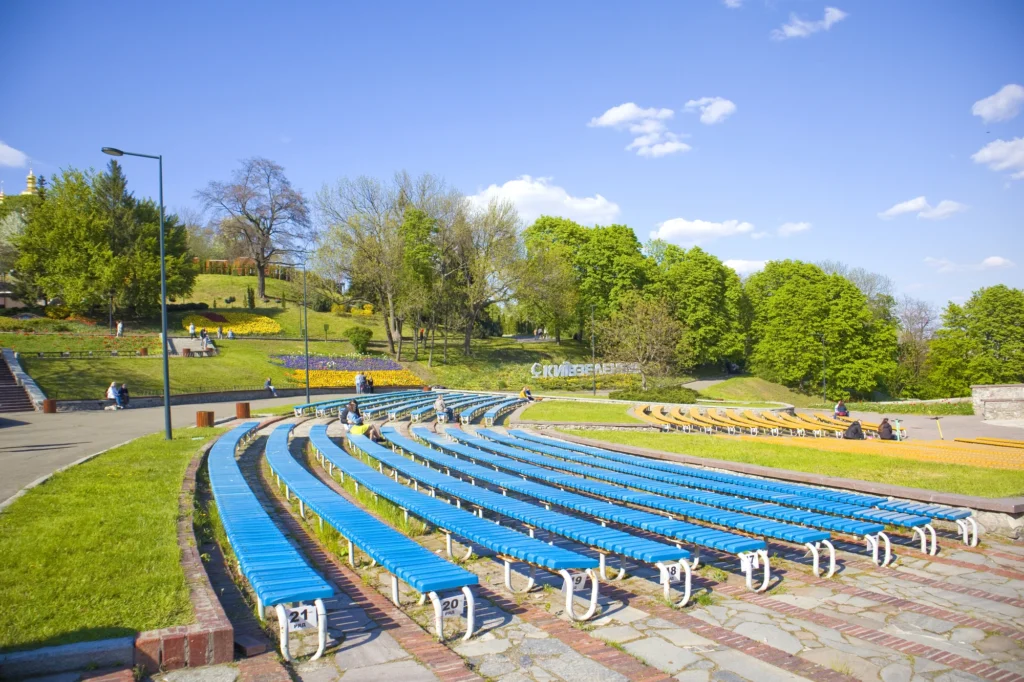
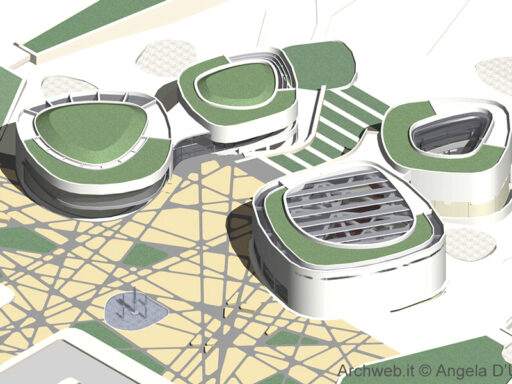
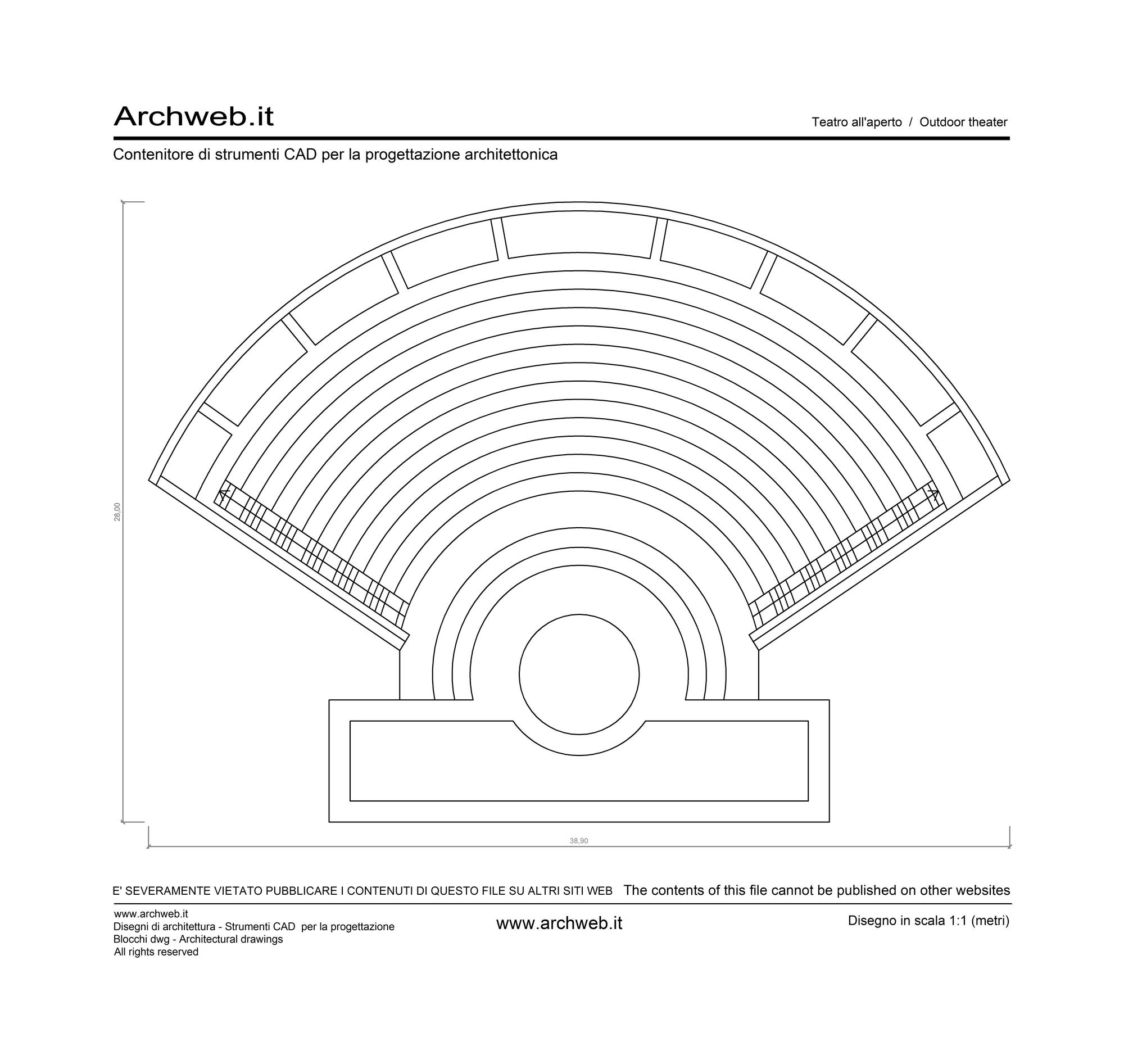
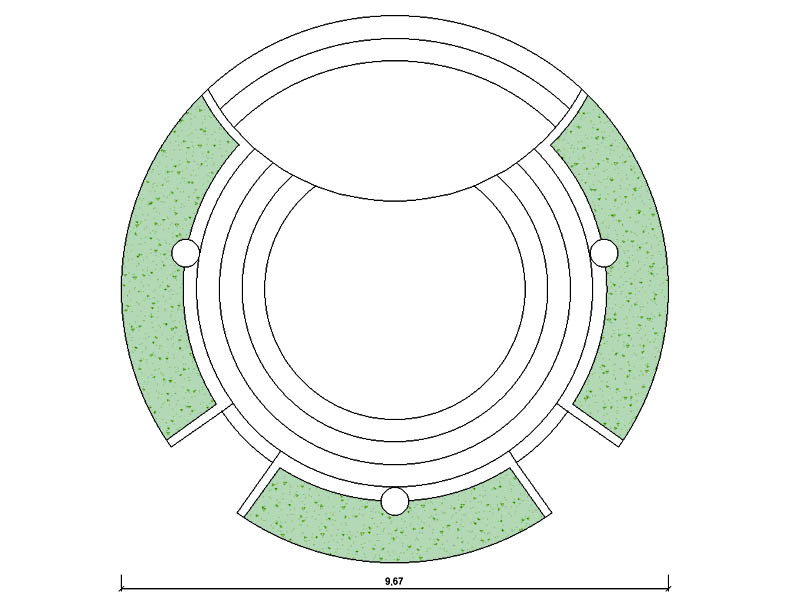
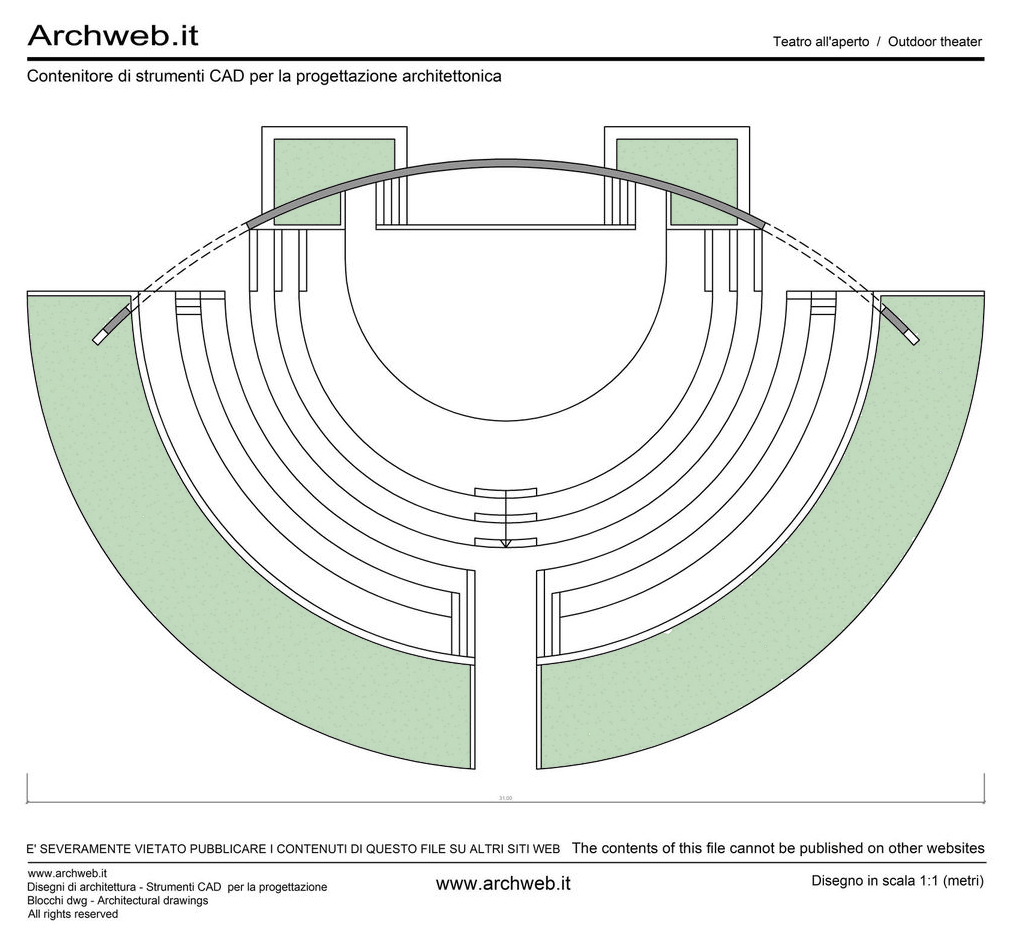
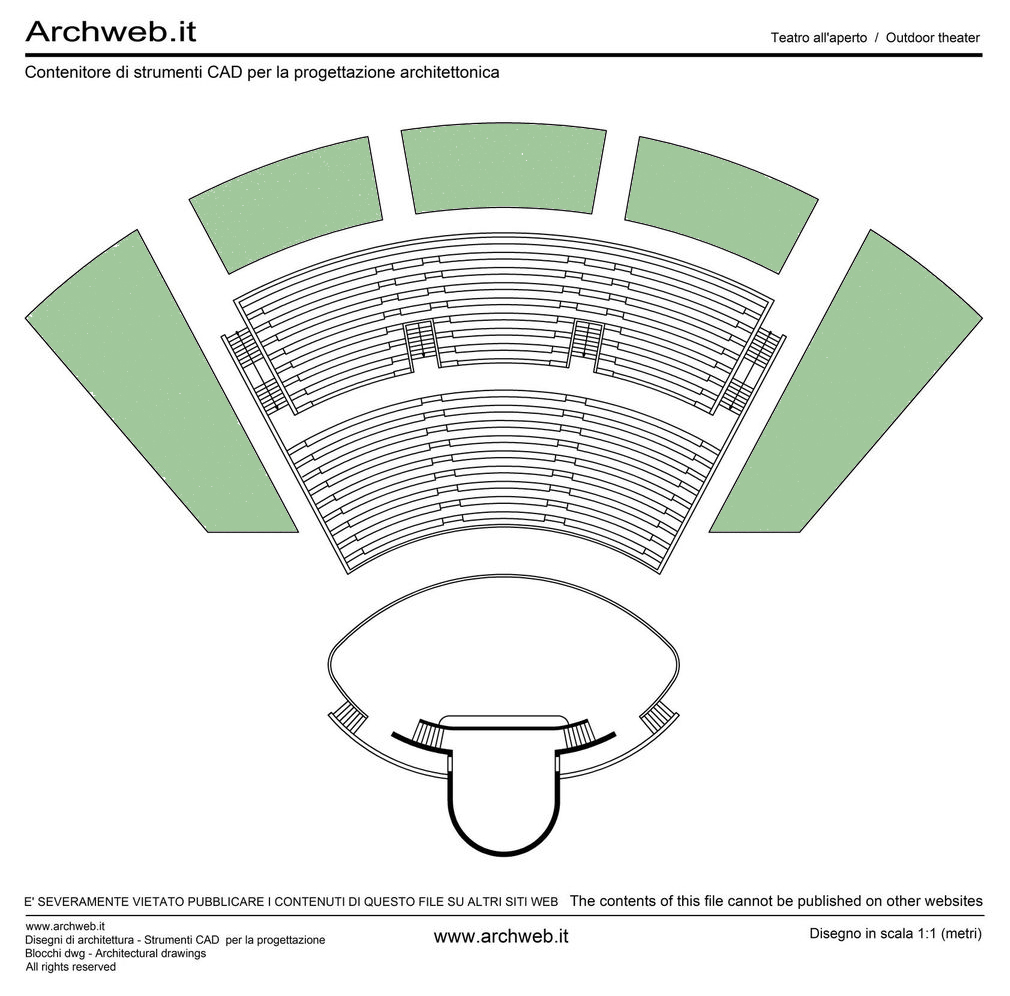
There are several types of outdoor theater projects that can be implemented in urban public parks. One of the most common is the stepped outdoor theater, where the audience can sit on stone or concrete steps to watch the performance. This type of theater provides good visibility for all spectators and creates a cozy and intimate atmosphere. Another type is the outdoor theater on grass, where the audience can lie down on the grass to enjoy the show. This type of theater is particularly suitable for informal and relaxed events. Finally, there are also temporary outdoor theaters, which are set up only for a specific season or event. These theaters can be built using prefabricated structures, offering flexibility and versatility in their design.
Photos by respective authors are courtesy of Depositphotos.com
Considerations for the design of an outdoor theater in a park
The design of an outdoor theater in a public park requires a number of important considerations.
- Location. It is essential to choose an area in the park that is suitable for the construction of the theater and can accommodate an adequate number of spectators.
- Orientation. It is important to consider the orientation of the theater with respect to the sun so as to make maximum use of natural light during daytime performances.
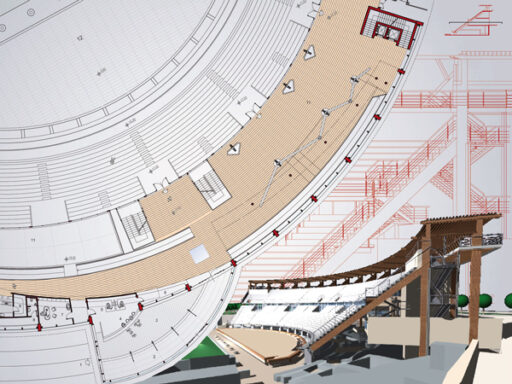
- Stage design and acoustics. These are crucial elements to consider.
- Accessibility. It is important to ensure that the theater is accessible to people with disabilities by providing accessible ramps and paths.
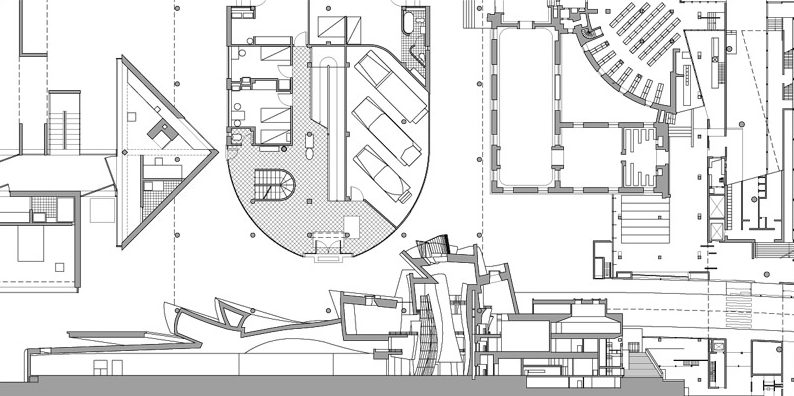
Examples of successful projects
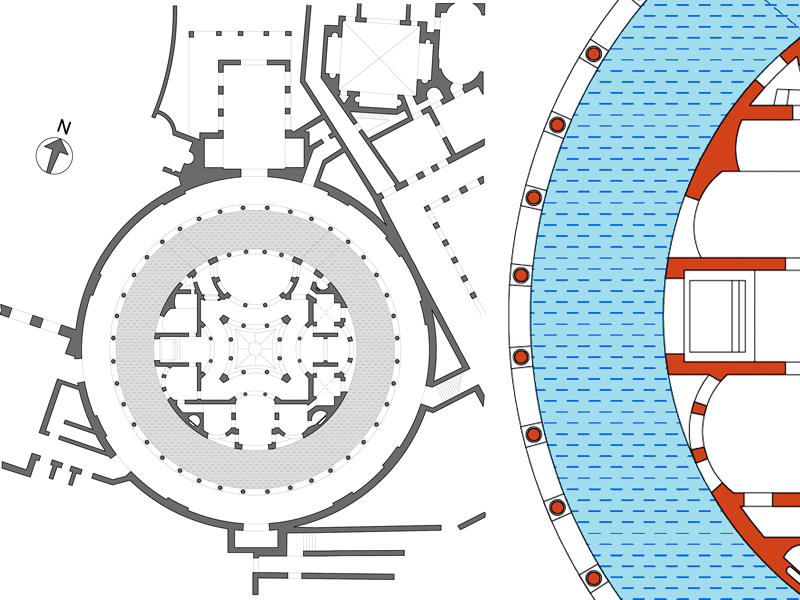
There are numerous examples of successful outdoor theater projects in urban public parks around the world. One of these is the Delacorte Theatre, located within New York City’s Central Park. This outdoor amphitheater is known for hosting free theatrical performances for the public in an informal and welcoming atmosphere, such as the New York Shakespeare Festival.
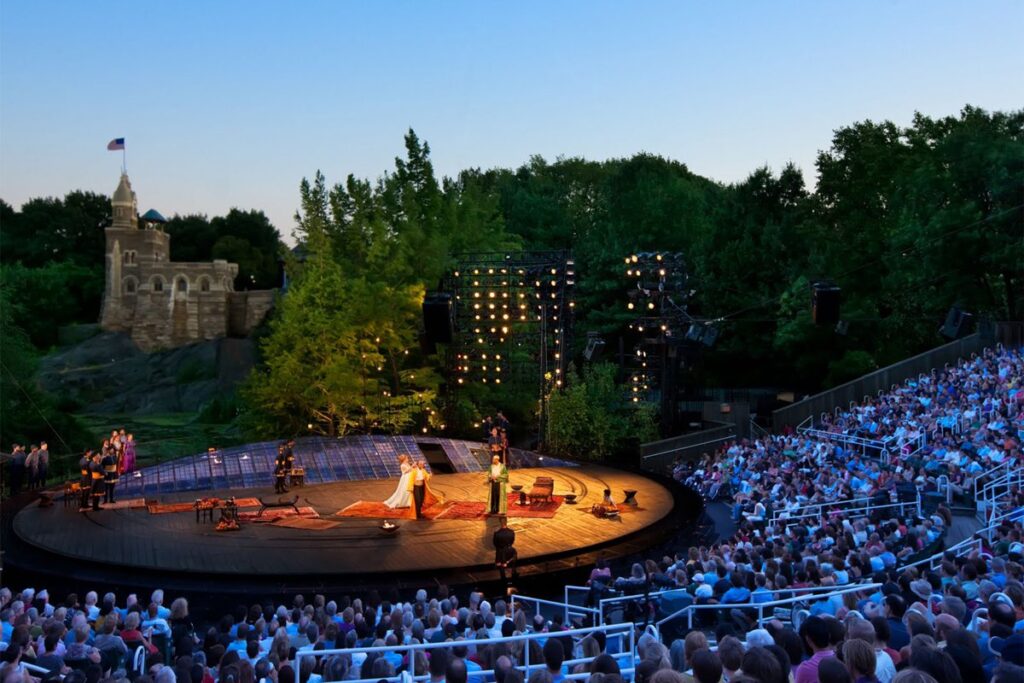

This example demonstrates how outdoor theater in public parks can be an effective way to bring art and culture into communities and engage audiences in a meaningful way.
Challenges and solutions for outdoor theater in parks
Despite its many advantages, outdoor theater in urban public parks can have some limitations.
- Weather. Unpredictable weather conditions can affect the scheduling of performances. To address this challenge, covered or partially covered facilities can be provided to allow shows to continue in rain or bad weather.
- Noise. Ambient noise can disrupt the quality of the theater experience. To address this challenge, acoustic screens can be used or locations within the park can be selected that are less disturbed by outside noise.
How to plan and implement an outdoor theater project
Planning and implementing an outdoor theater in a park requires careful consideration and organization.
The first step in the process is to determine the purpose and goals of the project. Do you want to provide entertainment for the community or raise funds for a charitable cause? Once the goals have been clarified, the next step is to identify a suitable location for the outdoor theater. Factors such as accessibility, availability of electricity, and the general atmosphere of the venue should be considered.
After choosing the location, it is essential to develop a detailed project plan. This plan should outline all the steps, resources, and timelines necessary for a successful outdoor theater project. It is critical to engage a team of knowledgeable individuals who can contribute their expertise in areas such as set design, lighting, sound, and event management. This team will be responsible for ensuring that all technical aspects of the project are well executed.
Another critical aspect of planning an outdoor theater project is obtaining the necessary permits and approvals. This may include public performance licenses, ensuring compliance with noise regulations, and acquiring any necessary insurance coverage. Consultation with local authorities and stakeholders is essential to ensure compliance with all legal requirements.
Once the planning phase is completed, it is time to implement the outdoor theater project. This involves coordinating with vendors and suppliers to source the necessary equipment, set-ups, seating, and other materials. It is important to have a clear communication plan to ensure that all team members and stakeholders are aware of their roles and responsibilities.
During the implementation phase, it is critical to regularly monitor progress and make necessary changes or course corrections. This may include solving technical problems, managing unforeseen challenges, or adjusting the project plan based on feedback from trials or tests.
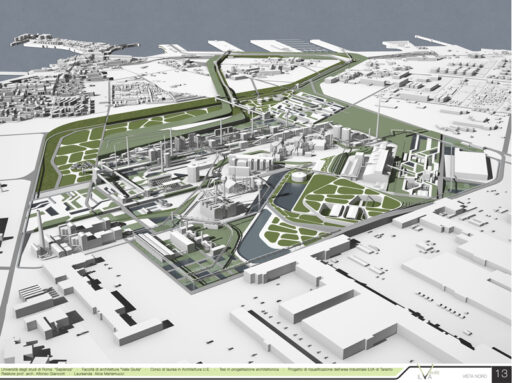
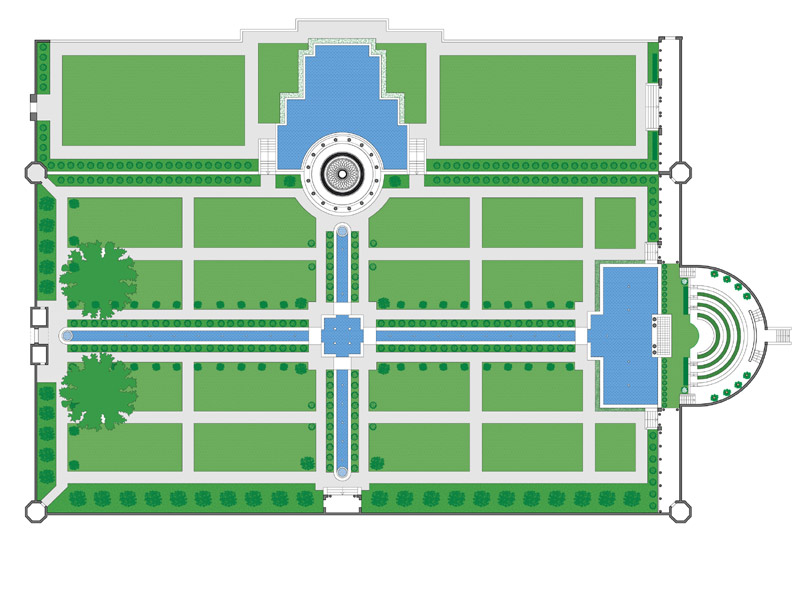
An interesting example from the point of view of inclusion in a green context is The Manzanares Linear Park, an urban green space located in Madrid, Spain. It extends along the Manzanares River for several kilometers. This park is an urban revitalization project that seeks to restore and improve the natural environment of the river, as well as provide recreational and leisure areas for the city’s residents and visitors.
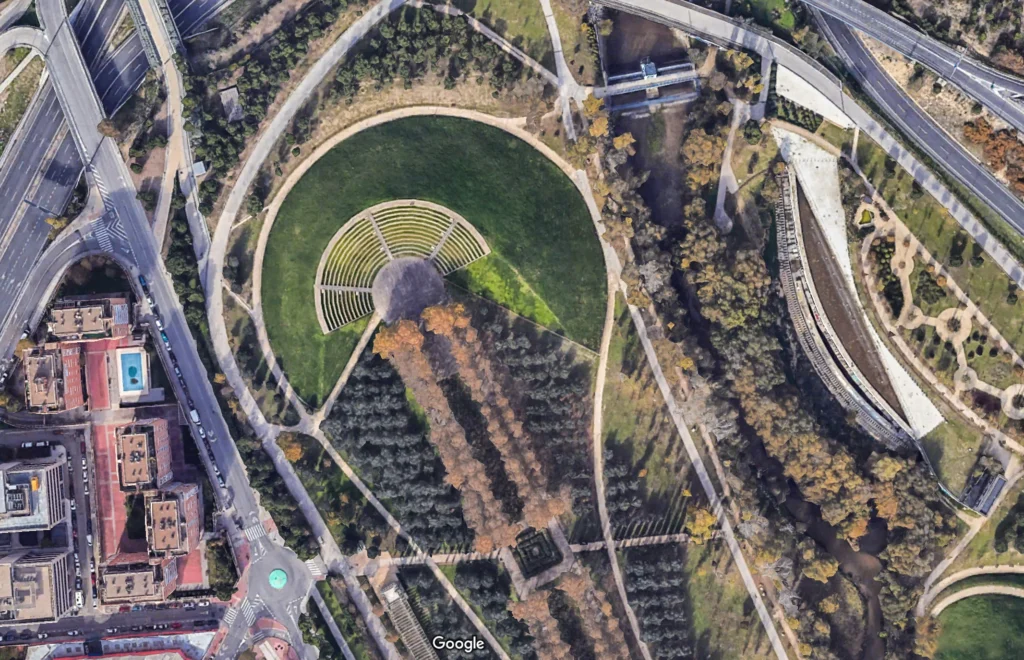

@ Google Maps
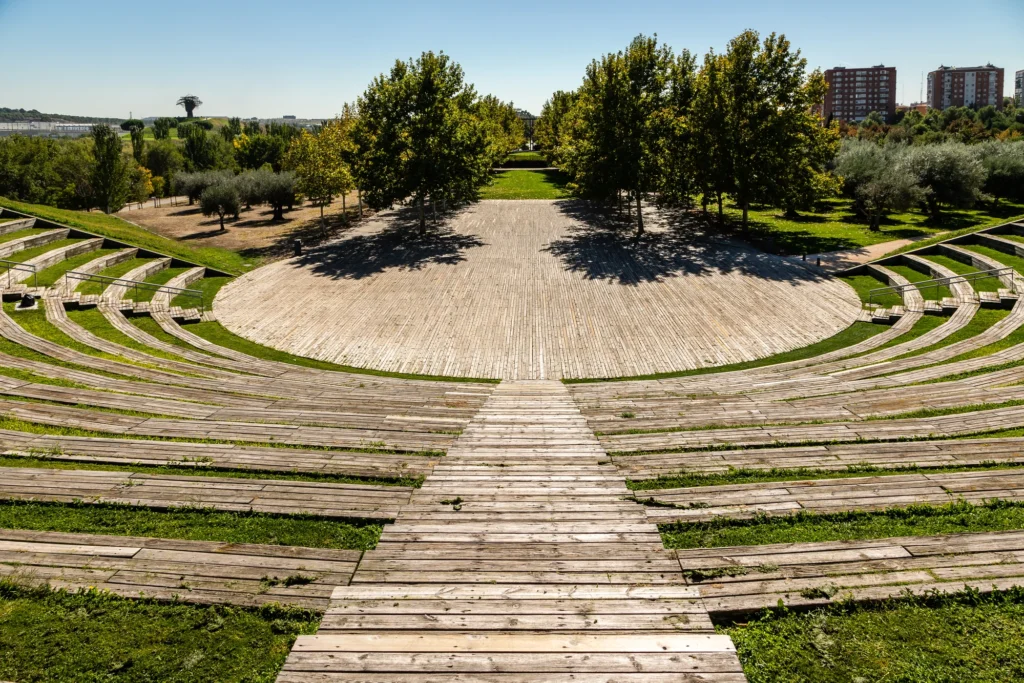

Photo by jslsvega su Depositphotos.com
Conclusions and future trends in outdoor theater design
Outdoor theater in urban public parks provides a unique opportunity to combine art and nature, creating an engaging and memorable theatrical experience for audiences. The unique characteristics of these spaces, their functionality and the many benefits they offer, make them an important element in the design of public parks. In the future, outdoor theater design is expected to move increasingly toward the use of sustainable and innovative technologies to create versatile and flexible theater spaces. In addition, it is expected that outdoor theater will continue to be an important tool for promoting art and culture in communities, contributing to people’s well-being and happiness.
Cover photo: Miralfiore Park Amphitheater (credit: teatridiPesaro.it)