Richard Neutra
Austrian architect (Vienna, 8 April 1892 - Wuppertal, 16 April 1970)
Richard Joseph Neutra (April 8, 1892 – April 16, 1970) was a Jewish Austrian-American architect. Living and building for the majority of his career in Southern California, he came to be considered among the most prominent and important modernist architects.
Neutra was born in Leopoldstadt, the 2nd district of Vienna, Austria Hungary, on April 8, 1892 into a wealthy Jewish family. His Jewish-Hungarian father Samuel Neutra (1844–1920) was a proprietor of a metal foundry, and his mother, Elizabeth "Betty" Glaser Neutra (1851–1905) was a member of the IKG Wien. Richard had two brothers who also emigrated to the United States, and a sister, Pepi Weixlgärtner, an artist who emigrated to Sweden where her work can be seen at The Museum of Modern Art.
Neutra attended the Sophiengymnasium in Vienna until 1910. He studied under Max Fabiani and Karl Mayreder at the Vienna University of Technology (1910–18), and also attended the private architecture school of Adolf Loos. In 1912 he undertook a study trip to Italy and the Balkans with Ernst Ludwig Freud.
In June 1914, Neutra's studies were interrupted when he was ordered to Trebinje ; he served as a lieutenant in the artillery in Trebinje until the end of the war. Dione Neutra recalled her husband Richard’s hatred of the retribution against the Serbs in an interview conducted in 1978 after his death: He talked about the people he met [i.e. in Trebinje … how his commander was a sadist, who was able to play out his sadistic tendencies … . He was just a small town clerk in Vienna, but then he became his commander
He took a leave in 1917 to return to the Technische Hochschule to take his final examinations.
After World War I Neutra went to Switzerland where he worked with the landscape architect Gustav Ammann. In 1921 he served briefly as city architect in the German town of Luckenwalde, and later in the same year he joined the office of Erich Mendelsohn in Berlin. Neutra contributed to the firm's competition entry for a new commercial centre for Haifa, Palestine (1922), and to the Zehlendorf housing project in Berlin (1923). He married Dione Niedermann, the daughter of an architect, in 1922. They had three sons, Frank L (1924–2008), Dion (1926–2019) an architect and his father's partner, and Raymond Richard (1939–) a physician and environmental epidemiologist.
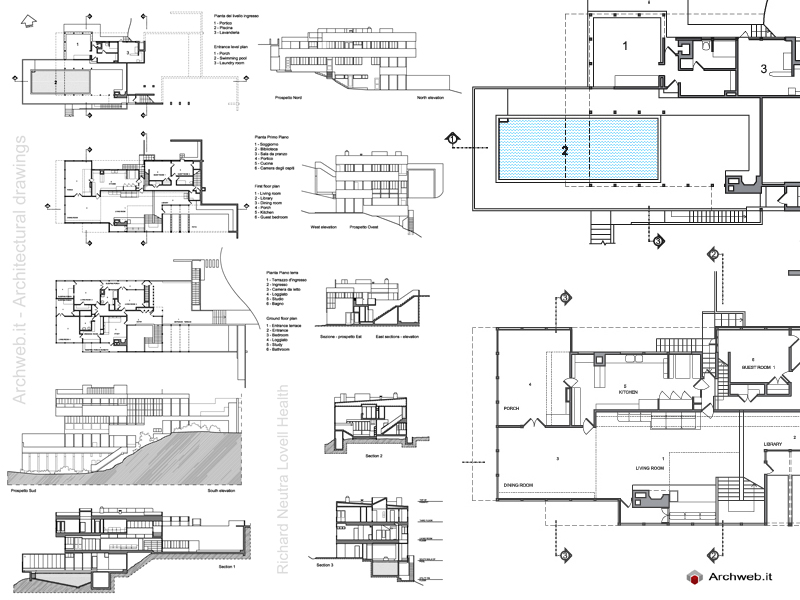
Neutra moved to the United States by 1923 and became a naturalized citizen in 1929. Neutra worked briefly for Frank Lloyd Wright before accepting an invitation from his close friend and university companion Rudolf Schindler to work and live communally in Schindler's Kings Road House in California. Neutra’s first work in Los Angeles was in landscape architecture, where he provided the design for the garden of Schindler’s beach house (1922–25), designed for Philip Lovell, Newport Beach, and for a pergola and wading pool for Wright and Schindler’s complex for Aline Barnsdall on Olive Hill (1925), Hollywood. Schindler and Neutra collaborated on an entry for the League of Nations Competition of 1926–27; in the same year they formed a firm with the planner Carol Aronovici (1881–1957) called the Architectural Group for Industry and Commerce (AGIC). He subsequently developed his own practice and went on to design numerous buildings embodying the International Style, twelve of which are designated as Historic Cultural Monuments (HCM), including the Lovell Health House and the Richard and Dion Neutra VDL Research House. In California, he became celebrated for rigorously geometric but airy structures that symbolized a West Coast variation on the mid-century modern residence. Clients included Edgar J. Kaufmann, Galka Scheyer, and Walter Conrad Arensberg. In the early 1930s, Neutra's Los Angeles practice trained several young architects who went on to independent success, including Gregory Ain, Harwell Hamilton Harris, and Raphael Soriano. In 1932, he tried to move to the Soviet Union, to help design workers' housing that could be easily constructed, as a means of helping with the housing shortage.
In 1932, Neutra was included in the seminal MoMA exhibition on modern architecture, curated by Philip Johnson and Henry-Russell Hitchcock. In 1949 Neutra formed a partnership with Robert E. Alexander that lasted until 1958, which finally gave him the opportunity to design larger commercial and institutional buildings. In 1955, the United States Department of State commissioned Neutra to design a new embassy in Karachi. Neutra's appointment was part of an ambitious program of architectural commissions to renowned architects, which included embassies by Walter Gropius in Athens, Edward Durrell Stone in New Delhi, Marcel Breuer in The Hague, Josep Lluis Sert in Baghdad, and Eero Saarinen in London. In 1965 Neutra formed a partnership with his son Dion Neutra.[6] Between 1960 and 1970, Neutra created eight villas in Europe, four in Switzerland, three in Germany, and one in France. Prominent clients in this period included Gerd Bucerius, publisher of Die Zeit, as well as figures from commerce and science. His work was also part of the architecture event in the art competition at the 1932 Summer Olympics.
Richard Joseph Neutra died on April 16, 1970, at the age of 78.
Source: Wikipedia…>>
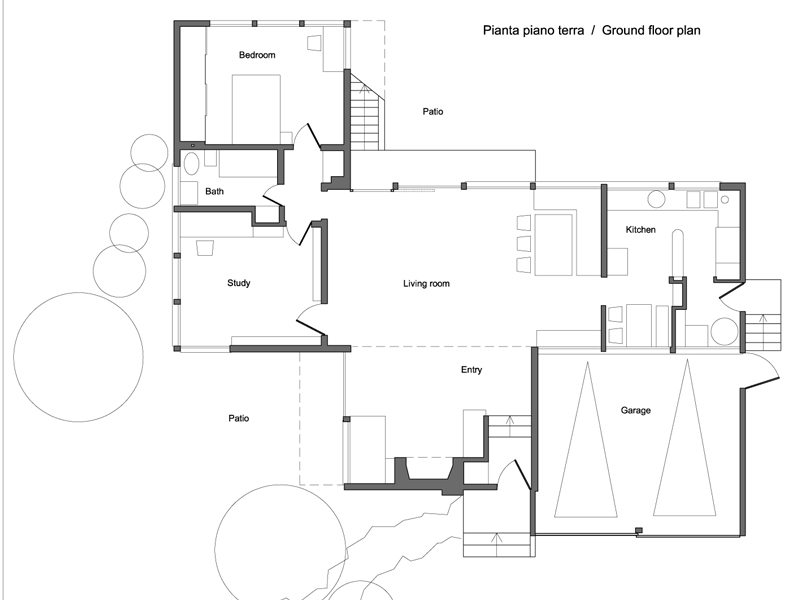
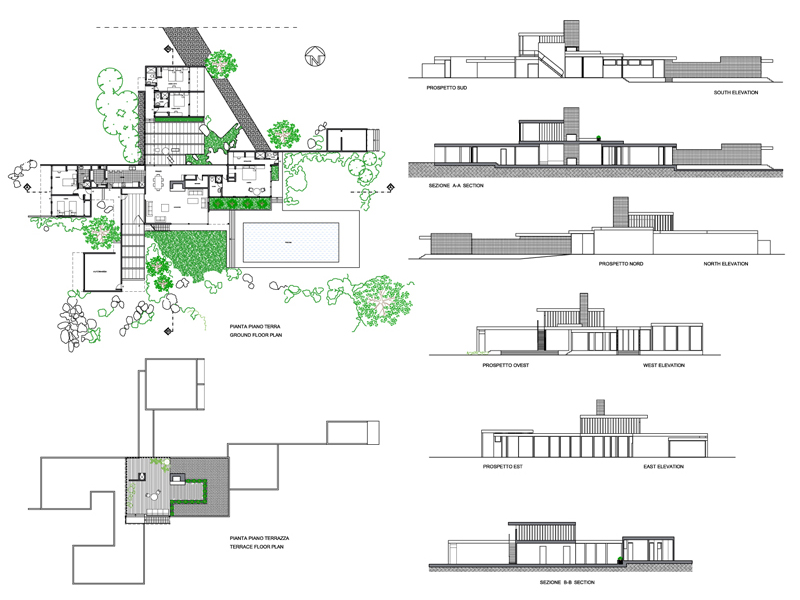
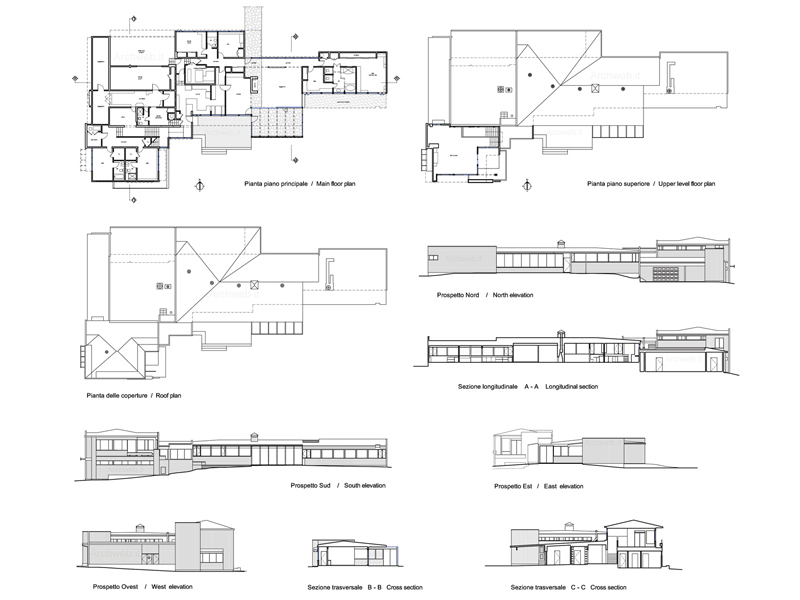
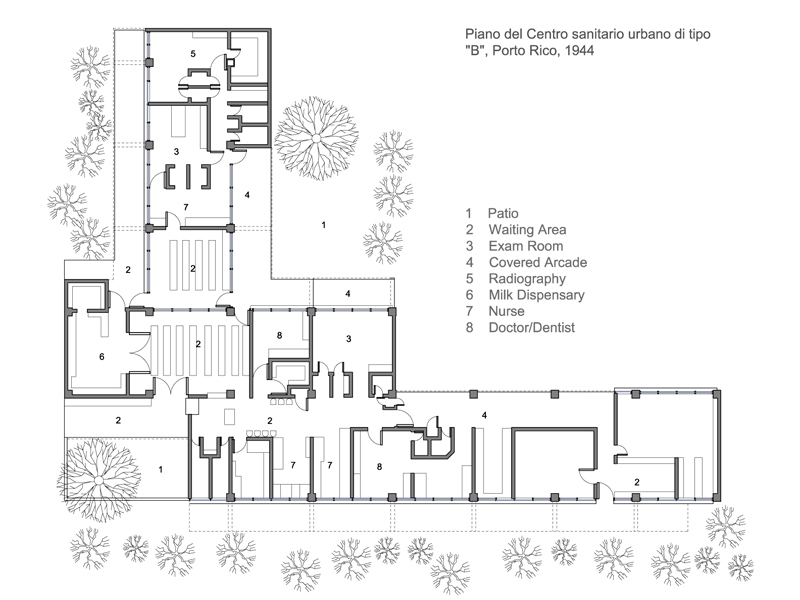
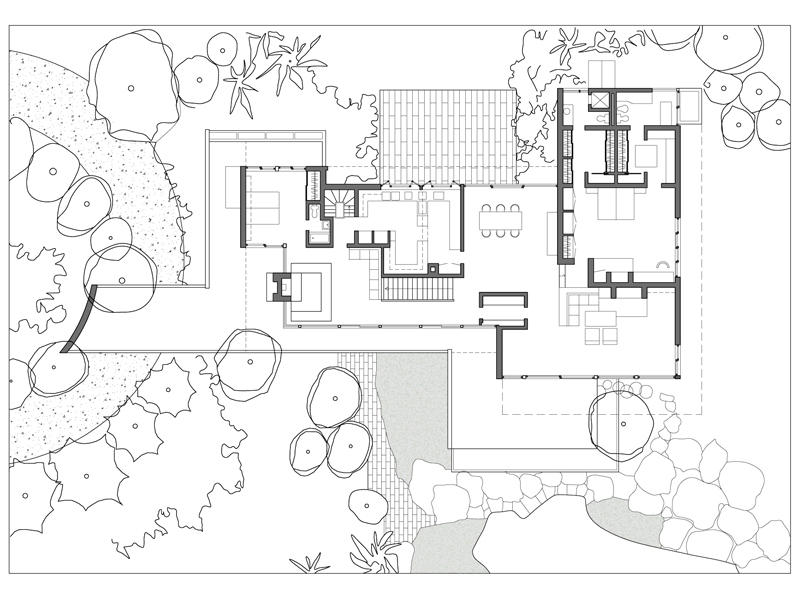
Works and projects
How the download works?
To download files from Archweb.com there are 4 types of downloads, identified by 4 different colors. Discover the subscriptions
Free
for all
Free
for Archweb users
Subscription
for Premium users
Single purchase
pay 1 and download 1