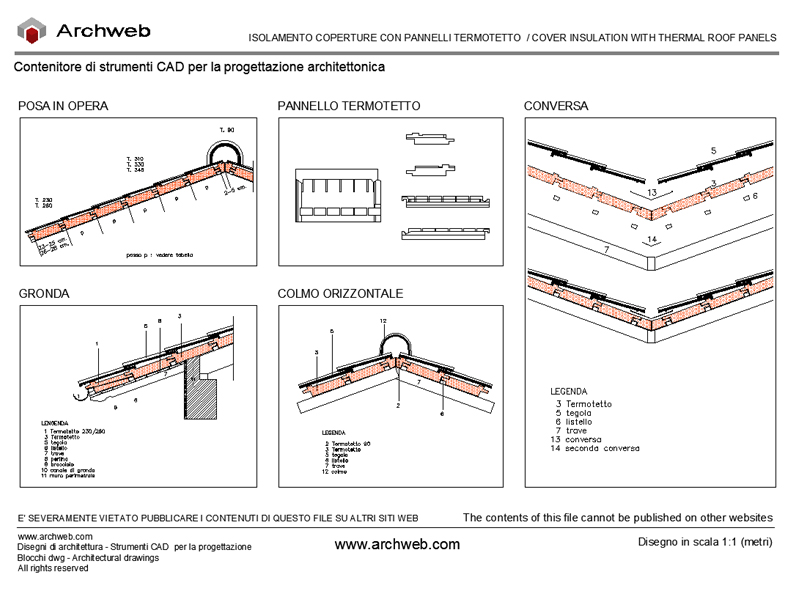
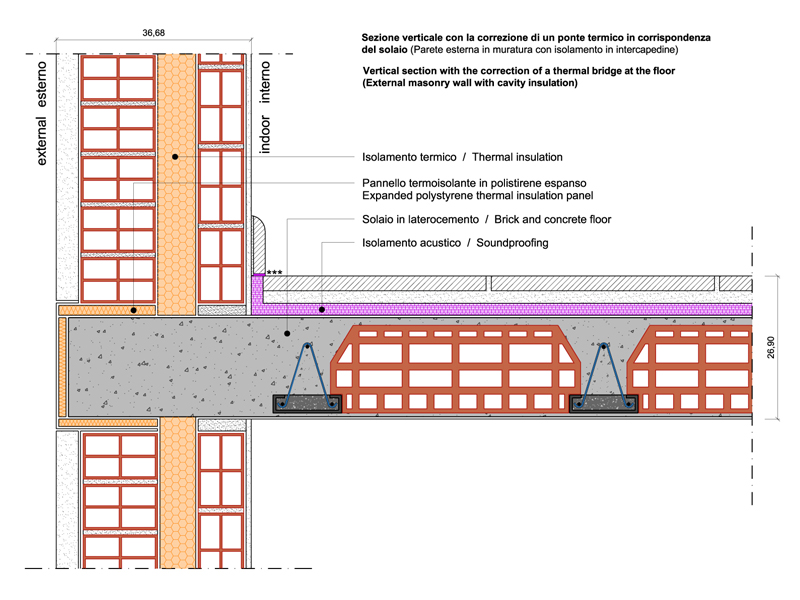
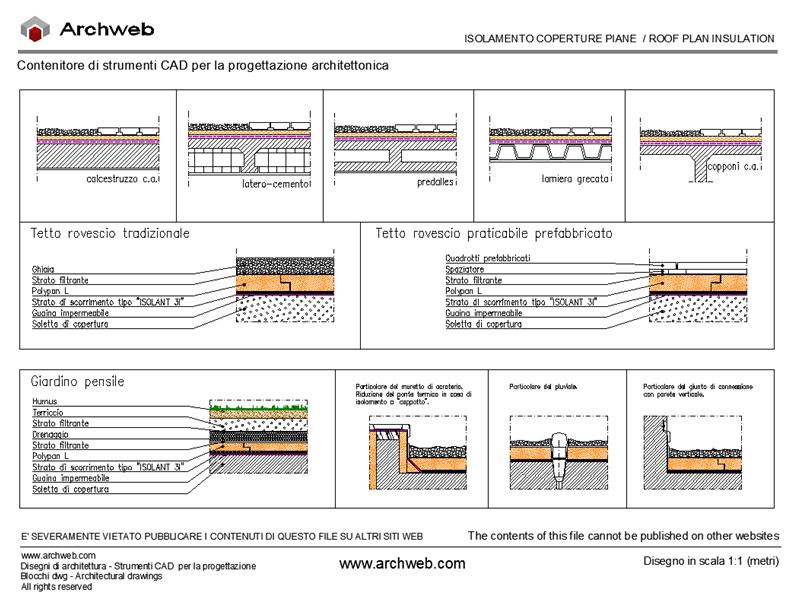
Materials for thermal insulation
The thermal insulation of buildings

Thermal insulation of buildings is essential to ensure living comfort.
Generalities
Thermally insulating a building, means putting in place all the necessary interventions to limit the flow of heat between the external and internal environment. These interventions, which involve the insertion of insulating materials, mainly affect opaque surfaces, i.e., vertical structures, intermediate horizontal structures and horizontal roof structures.
Ensuring high comfort conditions must be the designer’s goal regardless of whether it is a new construction or upgrading work on existing buildings.
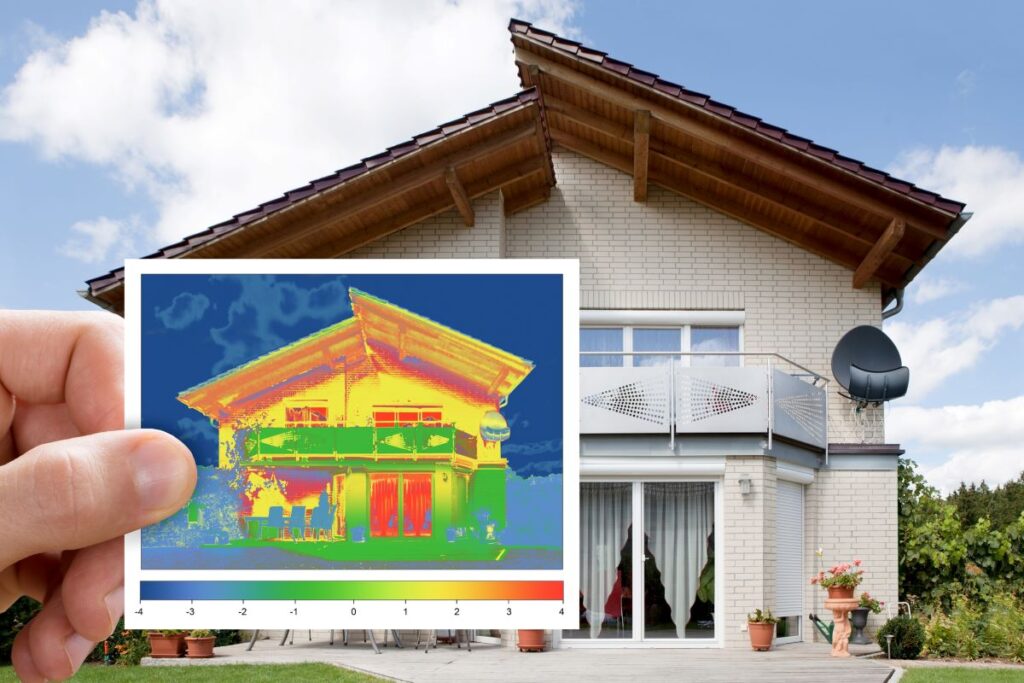

Normative reference
UNI ISO EN 7730:2006 (Ergonomics of Thermal Environments-Analytical Determination and Interpretation of Thermal Well-Being by Calculating PMV and PPD Indices and Local Thermal Well-Being Criteria) defines thermo-hygrometric well-being of the individual as “the mental condition of satisfaction with the thermal environment.”
Individual well-being, clearly depends on some subjective and therefore unquantifiable factors, and other factors external to the individual and therefore quantifiable (e.g., temperature, or humidity).
To ensure the right thermo-hygrometric conditions within a room, one must carefully design each part of the envelope to avoid the presence of thermal bridges, and critically choose the right insulation materials.
Design solutions
The design solution can never be unique to be adapted for every building.
In fact, several factors must be considered:
- climatic reference context
- type of intervention (new building or existing building)
- intended use (public or private)
- economic availability
Once the above factors have been defined, we can study the right stratigraphy to be carried out or the interventions needed to ensure thermal insulation of the envelope.
Insulation of vertical opaque structures, can be performed either from the exterior side of the wall or from the interior side.
Insulation from the outside involves the construction of thermal coats, ventilated walls or the laying of insulating plasters. Clearly, interventions such as these will not change the available interior space, but they do require skilled installation.
Insulation from the inside, on the other hand, consists of “lining” the wall with insulating panels. Obviously by acting from the inside, adding an additional layer to the wall, the space will be resized.
If the building is made with a cavity, you can think of blown-in insulation, already discussed here:
https://www.archweb.com/en/insulation-by-blowing/

Insulation materials: types
When choosing an insulation material, a number of parameters must obviously be taken into account. The most important is obviously the thermal conductivity λ [W/mK]. Thermal conductivity expresses the ability the material has to transmit heat. Low values of λ, indicate a material with.
Different types of insulation materials are found on the market. They can be distinguished according to their origin. Specifically, we can enclose them in three macro categories:
- Materials of natural origin
- Materials of mineral origin
- Materials of synthetic origin
Natural orginine materials
Natural materials, are mainly of plant origin. They come from raw and renewable materials. They have production and installation processes that are not harmful to humans. They are generally used for exterior coats, interior wall insulation, attic insulation and being non-toxic also for interior wall insulation.
They fall into this category:
- Wood fiber
- Hemp fiber
- Cellulose fiber
- Cork panels
- Jute fiber panels
- Flax fiber
- Corn fiber
- Coconut fiber
Materials of mineral origin
Materials of mineral origin are the most widely used in construction. They are obtained by processing rocks and their use depends on their composition and structure (fibrous, honeycomb, cellular).
They are generally used for coats, ventilated facades, false ceilings and floors.
They fall into this category:
- Glass wool
- Rock wool
- Expanded clay
- Expanded perlite
- Felts
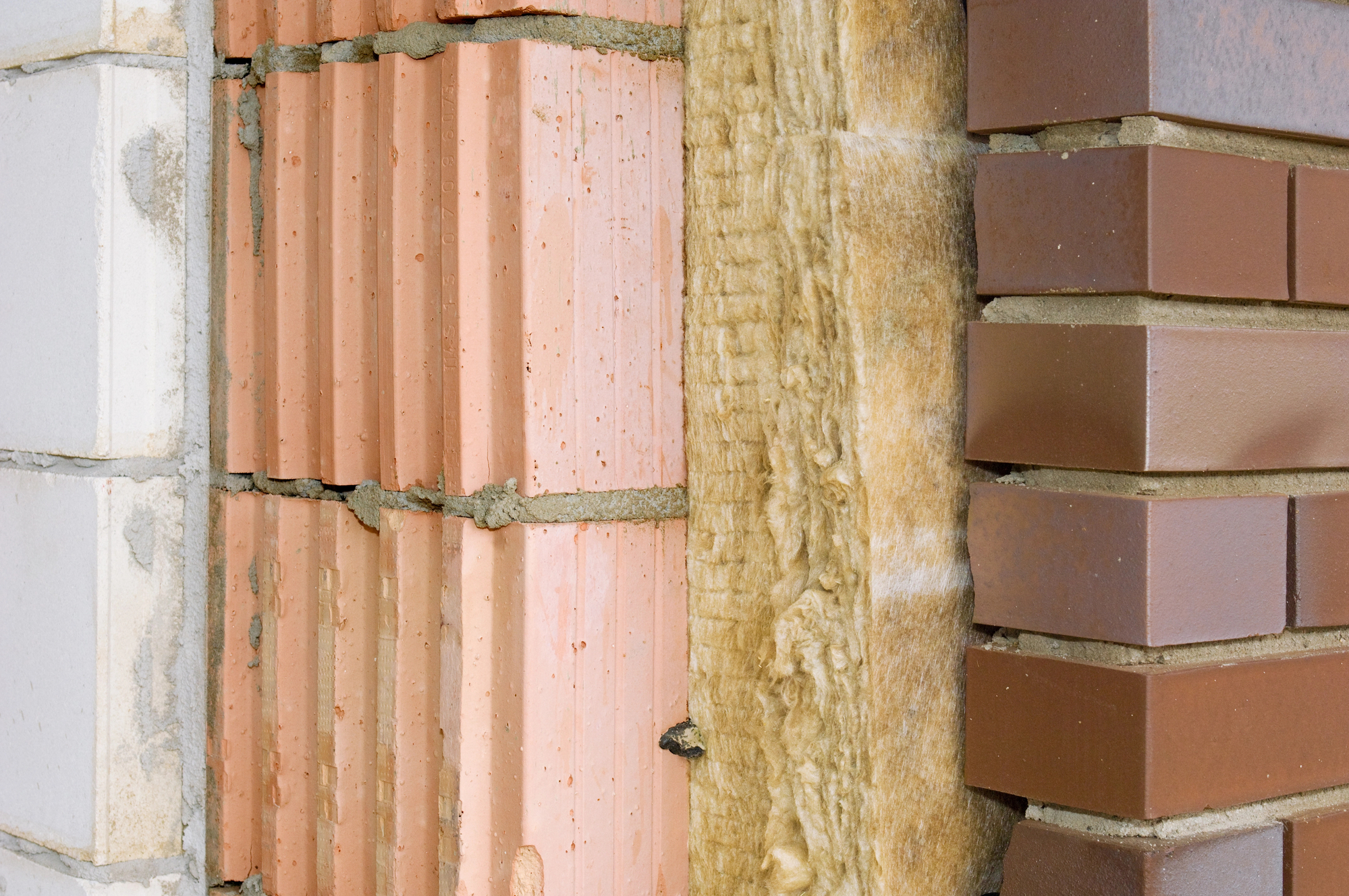

Materials of synthetic origin
Materials of synthetic origin, have been and to some extent still are widely used in construction. Unfortunately, many studies in recent years, have shown how the use ti such materials is harmful to the environment, to humans and above all presents high difficulties in recycling. Therefore, today where greater attention to the environment is not only a choice but also an obligation, other types of insulation materials are to be preferred. They fall into this category:
- EPS Expanded Polystyrene
- XPS Extruded polystyrene foam
- Polyurethane
- Reflective rolls
Commercially available formats
The various insulation materials, can be found on the market in different formats.
- Panels: can be rigid or semi-rigid to be fixed to the substrate
- Rolls: placed generally in crawl spaces or false ceilings
- Foam: are sprayed with appropriate equipment into air chambers
Clearly, the choice of one insulator over another also takes into account available formats and application methodology.

CAM (Minimum Environmental Criteria)
With Ministerial Decree 11/10/2017, the Minimum Environmental Criteria come into force in Italy.
The goal of CAM is to ensure environmental performance above the industry average through rationalizing consumption and making buildings more sustainable and efficient.
The decree lists a number of verifications that insulation materials must also meet.
However, there is no CAM certification, to be given to materials that meet these requirements. It will suffice to look for other types of environmental certifications, such as the EPD (Environmental Product Declaration) certification, which attests to a product’s environmental characteristics.
Compliance with CAM is a good indicator and, in addition, is a requirement for access to tax bonuses.
Cover photo is by kalinovsky at Depositphotos.com