Ventilated glass facades
Aesthetic enhancement and energy containment
The glass that covers the entire facade performs the function of a continuous wall in which the openings can be exposed, highlighted, or hidden in the homogeneous surface. The glazed surfaces can therefore also correspond to blind walls of the building and the function of the wall is to protect the internal and aesthetic layers. In the past, the glass walls corresponded to a strong heat loss or an accumulation of heat due to the greenhouse effect, now there is the possibility of creating facades with ventilated systems that have the advantage of meeting the requirements of insulation, lightness and architectural value.
Advantages
- Aesthetic and architectural features of the facades.
- Realization of the coating with a dry method, which allows, over time, to ensure the replacement of elements in a timely manner, without intervening on the entire wall.
- Energy saving, which results in excellent yield and the elimination of thermal bridges.
- Excellent response to rain and atmospheric agents, with elimination of condensation.
- Acoustic insulation determined by the stratigraphy of the ventilated wall.
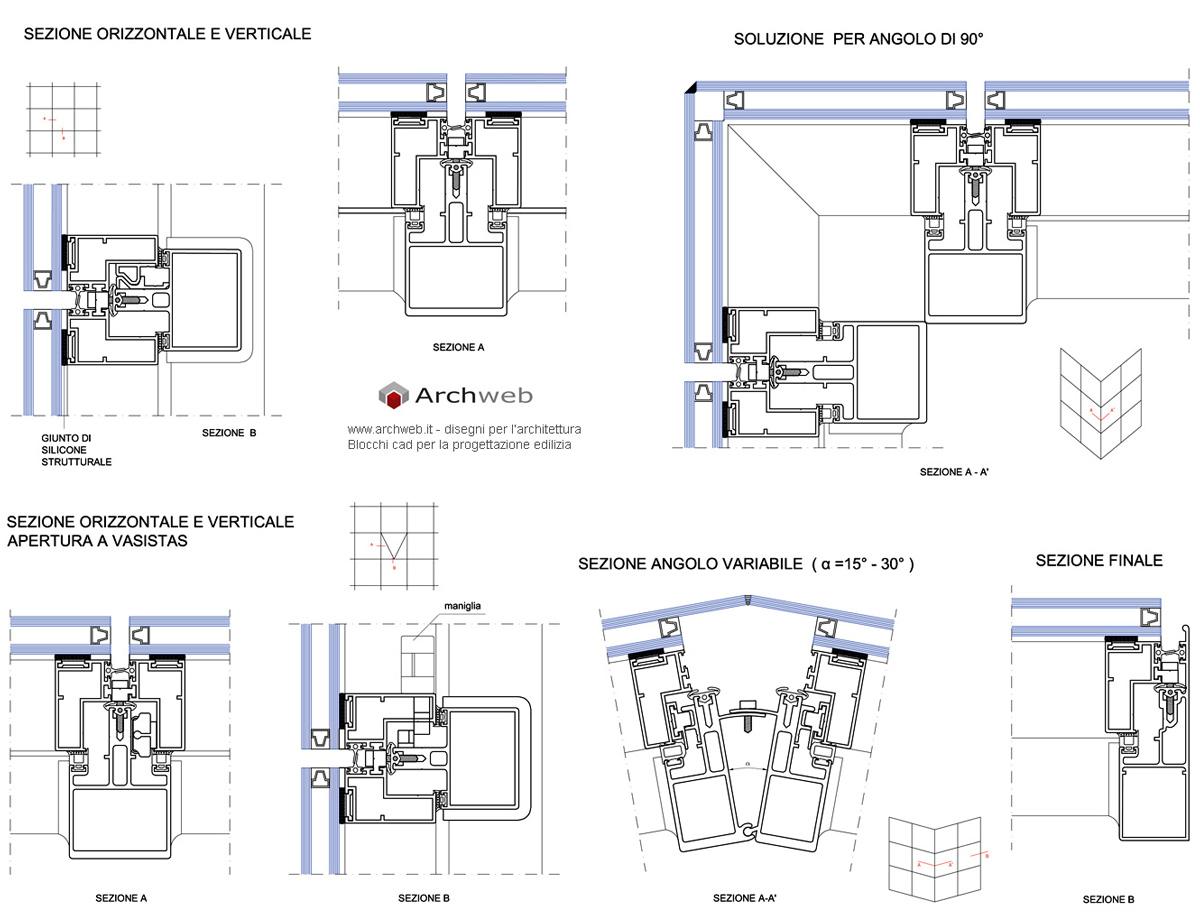
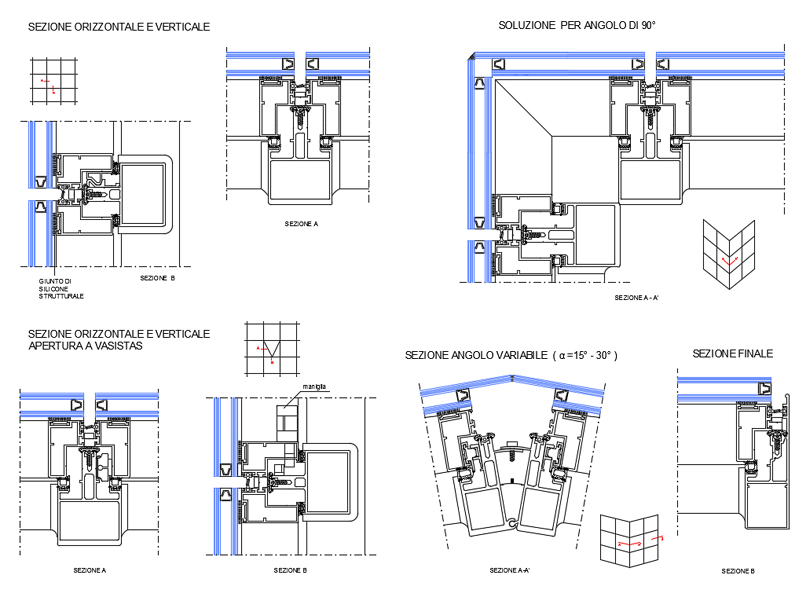
The panels and the related thermal insulation are fixed to the walls through substructures anchored to the perimeter surfaces of the building and in the cavity the air circulation generates the chimney effect which allows to improve energy performance.
Like the light duvets that can protect us from the cold, the ventilated walls cover the entire building, eliminate thermal bridges and offer an excellent response to the damaging effects of humidity.
Composition of the ventilated wall
- External insulation on the perimeter wall of the building.
- Ventilated air chamber.
- Supporting substructure of the external cladding, usually made with a metal / wooden support grid or with punctual supports
- Glazed external facing.
Among the insulating materials, mineral ones are preferable and the anchoring elements must be specially made to contain heat losses.
Characteristics of external insulation
- Planarità assicurata alla superficie, di solito ottenuta utilizzando pannelli isolanti rigidi.
- Traspirabilità, in modo da evitare i fenomeni di condensa, anche con inserimento di barriere al vapore.
- Caratteristiche anti-muffe e resistenza alla durabilità.
- Resistenza al fuoco, per evitare che l’effetto camino faciliti la propagazione del fuoco all’intera superficie dell’edificio.
- Resistenza ai raggi UV e alle temperature elevate.
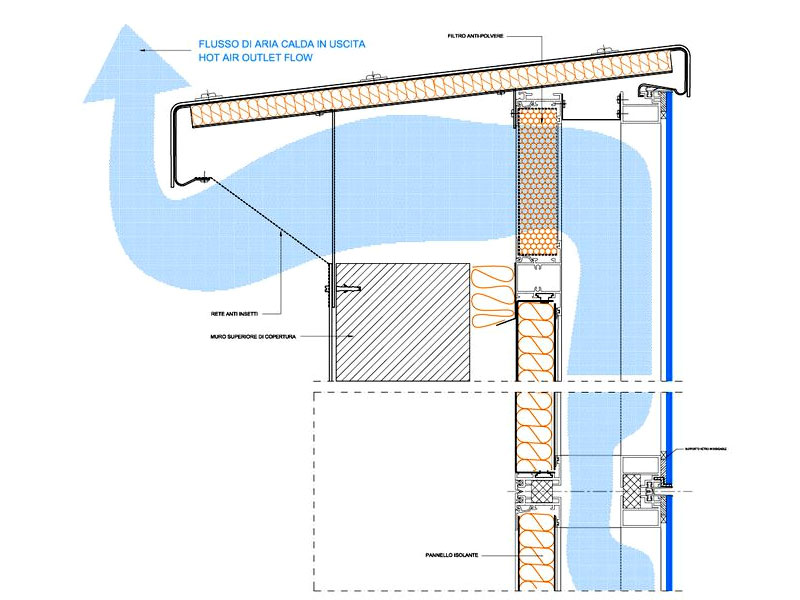
Ventilation gap
The ventilation layer, present between the insulating layer and the external cladding, uses the chimney effect that is generated due to the temperature differences and natural convective motions by virtue of which hot air, which has a lower density, tends to flow upwards, while the cold one goes downwards.
The glass walls are partially able to reflect heat to the outside and the residual heat is disposed of by the air chamber which generates a convective motion of the air, the so-called “chimney effect”.
This is caused by the temperature difference of the air in the cavity and is regulated by the openings at the base and top; the operation is activated by the heating which, through the external wall, is transferred to the cavity generating the upward motion, allowing, thanks to the ventilation of the wall, a decrease in temperature. The cavity also performs the function of energy containment during the winter season and the external facing protects the internal layer, keeping the internal temperature of the building in balance, leaving it dry and free of thermal bridges.
The cavity, usually between 3-5 and 7 cm, must be sized both to avoid excessive convective motions and too narrow channels that prevent proper ventilation.
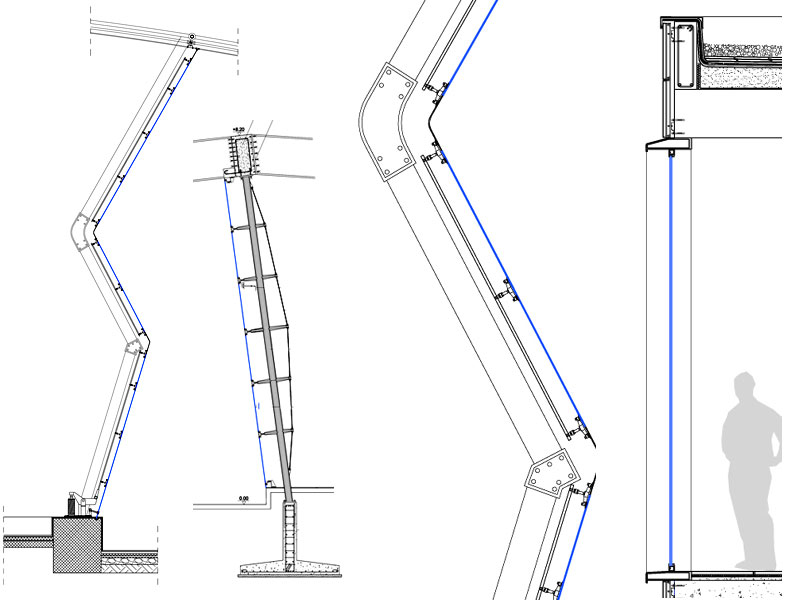
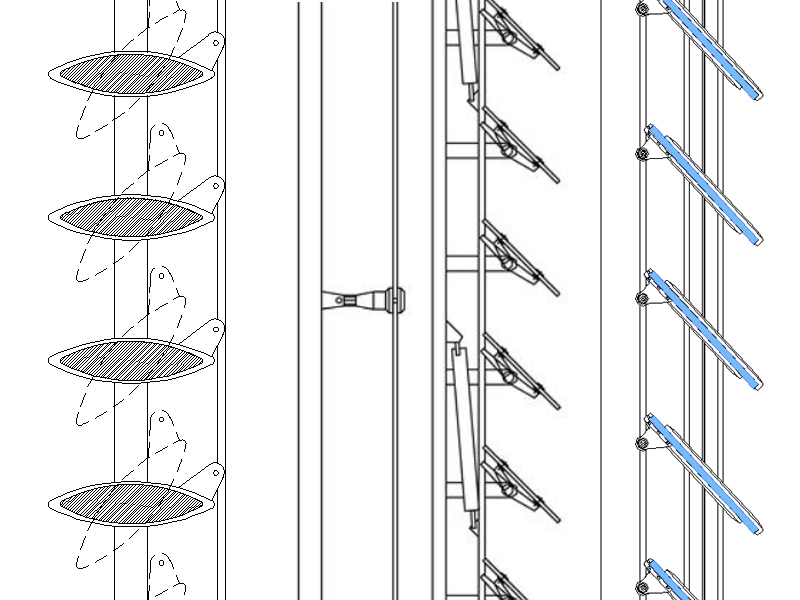
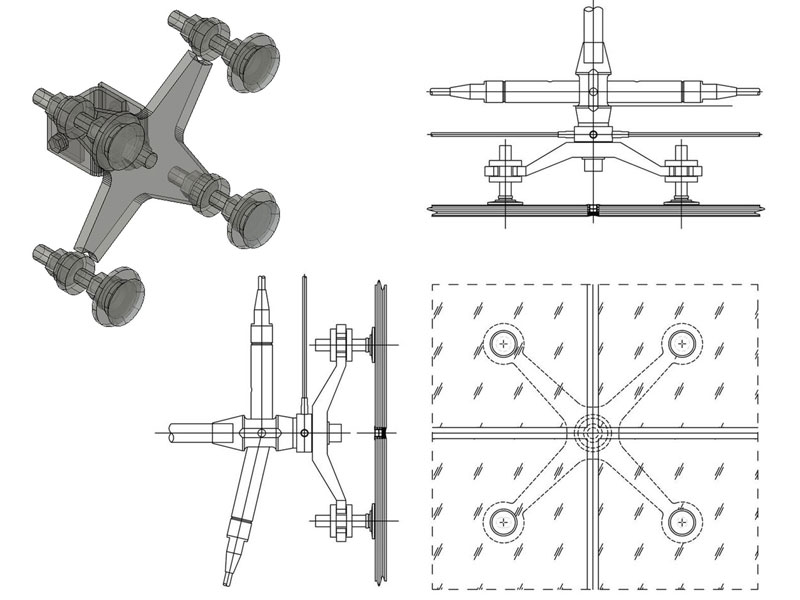
Support substructure and relative anchors
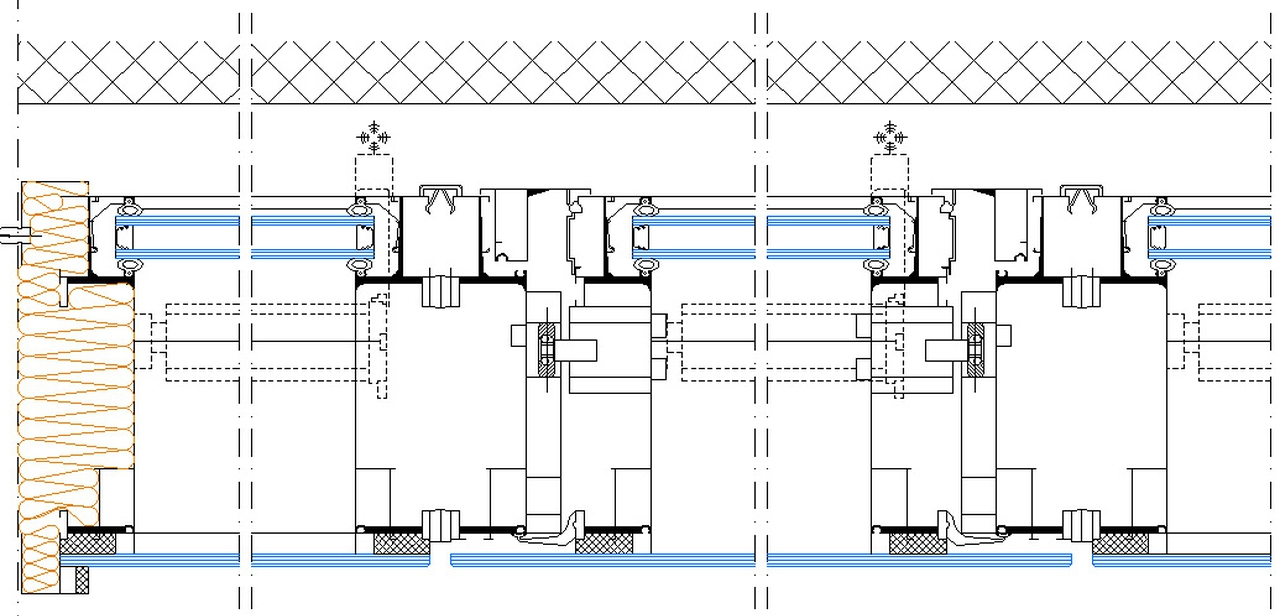
Usually the substructure is made with a lattice of metal or wood supports, of the upright, cross-member, upright and cross-beam type, or with point supports. The substructure and the relative anchoring hooks must be sized and evaluated in relation to the weight to be supported and the limit conditions, determined by the wind and seismic agents.
The technology with which the fixings are made can be visible or hidden; it is a dry system with special stainless steel hooks.
The UNI 11018: 2003 standard (Coatings and anchoring systems for mechanically mounted ventilated facades) dictates the characteristics of the systems that must be equipped with adjustment elements to ensure the flatness of the installation, usually thanks to elements in aluminum or stainless steel or zinc-titanium. Among the types of fastening, isostatic, point-like (clamps, brackets), hyperstatic, widespread, with frame uprights are preferred
External coating
Among the cladding systems, the glass sheets are able to give extraordinary aesthetic effects, giving lightness and transparency because they allow to obtain surfaces in which the opening elements of windows and French windows are inserted into the curtain wall. These systems can be made by means of prefabricated structures with visible or concealed aluminum profiles, completely invisible. The sheets can alternate surfaces with glass and other material or glass surfaces with different coloring and surface treatment, bring transparent, semi-transparent or mirror-type glass elements. Thanks to the new characteristics of the materials, it is possible to obtain laminated glass capable of filtering solar radiation
It is possible to obtain effects of total coplanarity that completely hide the substructure frame from view and the glass can be particularly efficient both from the point of view of thermal and acoustic insulation. These walls maintain the characteristics of protection from atmospheric agents, favor the breathability of buildings, thanks to the cavity that preserves the internal structure from humidity.
This technology is based on the modularity of the elements used and, in the event of damage to the external facing, each single slab can be replaced.
Among the most innovative systems, they also offer the possibility of creating facades that use solar energy to obtain electricity, through photovoltaic technology.
The windows can be solar control and low-emissivity glass, which allow better environmental comfort and substantial energy savings, with the enhancement determined by the large glass surfaces and the benefit of passive solar gain.
The laminated windows reduce the possibility of accidental breakage by protecting people and things.There are also special self-cleaning glasses, used in the surface layers of the stratified elements, to contain management costs and characteristics over time.
Performance
Behavior to water
The glass walls preserve and protect from the action of water by isolating the underlying walls, while also preserving the underlying insulation. Any filtered water is disposed of from the cavity. The formation of condensation in the interior is limited and abolished thanks to the breathability of the insulation, the thermal action determined by the combined provision of the insulation and the ventilation chamber.
Behavior to fire
The cavity, the insulation, the support substructure and the relative anchoring hooks, the envelope, must guarantee both individually and as a whole good behavior in the event of a fire, responding to the Circ. 5043 of the Ministry of the Interior.
Behavior in the wind
The plates used, in their shape and size, but also the fixing and anchoring systems, must be checked for both compression and traction stresses and for fatigue resistance.
For the calculation and sizing always consider the worst climatic conditions, using the greatest possible precautions.
Thermal and acoustic insulation
The external insulation and the ventilated cavity guarantee good thermal comfort in every season. Compliance with the DPCM 5/12/1997 is achieved by reflection, absorption and acoustic transmission, thanks to the stratigraphy of the ventilated facade. To determine the thermal transmittance value of the vertical walls, the checks should take into account seasonal variations, considering the reflections caused by solar radiation and the effect of ventilation and the insulating layer, evaluating the possibility of modulating the inlet and expulsion grids of the air.