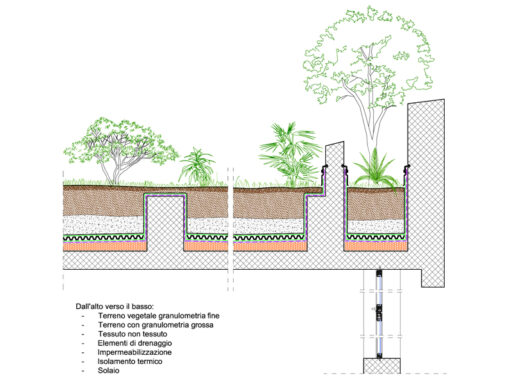
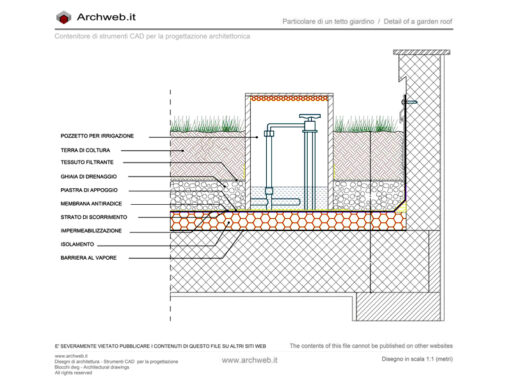
Hydroponic cultivation
Hydroponic cultivation. Types and techniques for cultivation
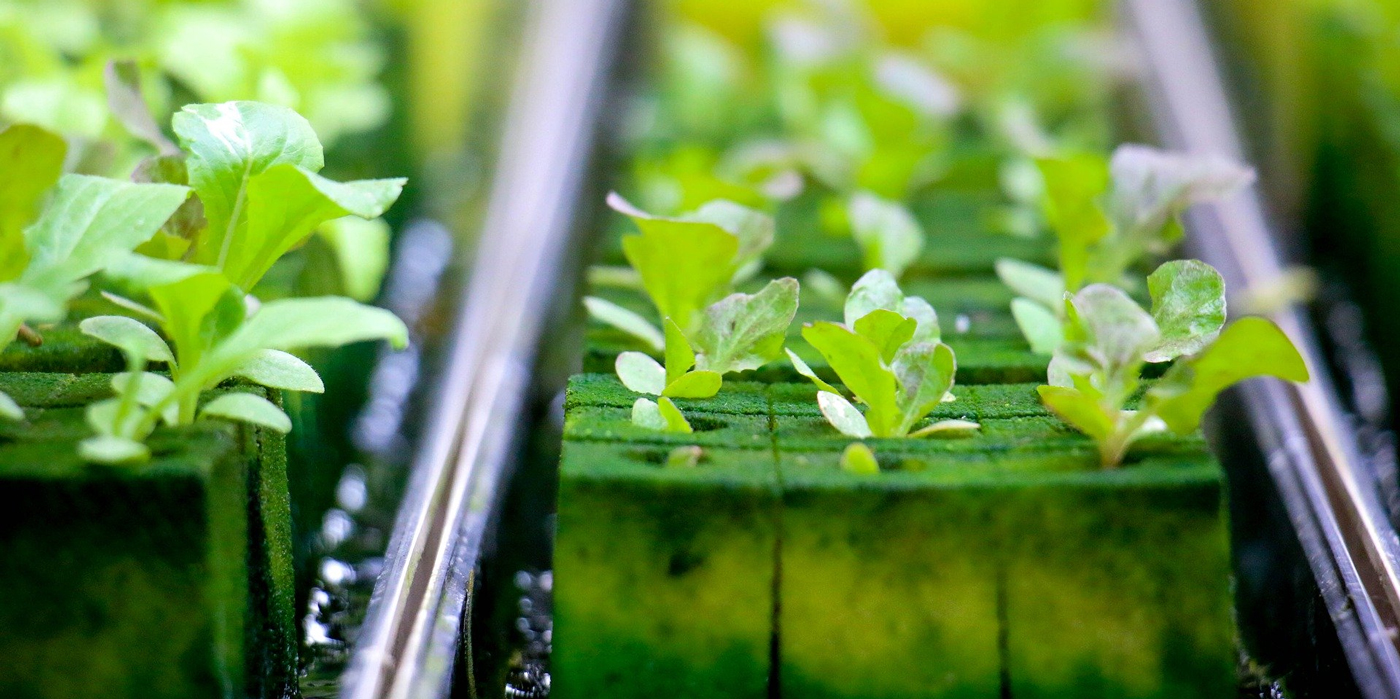

Hydroponics is a plant cultivation technique that consists of using aqueous solutions rich in nutrient salts instead of the soil. They are crops that extend on a scale tank as they have the possibility of growing in a protected environment, without competition between species and predators.
The first known traces of hydroponic cultivation can be found in the crops of the ancient Egyptians (Resh, 2001), in the gardens of Babylon and the Aztecs in Mexico (Jensen 1997)
The main difficulty for this technology is given by the cost of the plant, the maintenance of the plants and the specialized manpower required to run the system. Recent studies aim at the search for more sustainable modern technologies to bridge the gap.
Hydroponics consists in supporting cultivation through automation systems for climate and transpiration control and cultivation in greenhouses. Hydroponic systems however, have limitations of use.
Features and limitations of hydroponics
With hydroponics it is possible to provide the inputs necessary for cultural needs, avoiding the risk of attack by soil pathogens.
The use of closed systems therefore increases the risk of a spread of pathologies linked to the root system. To avoid this it is necessary to disinfect with exposure to UV rays, AND with heat (pasteurization).
Out-of-soil crops are also a useful tool to control plant production growth through controlled management of nutrient supply, but it increases the stress for the culture.
The first use in recent times dates back to the 1920s, for commercial purposes, the goal was to solve the problems related to the salinization of soils and soil pathogens. The research was conducted at the California Agricultural Experiment Station by W.F. Gericke who first used the term “hydroponics” from the Greek “Idros”, water and “ponos” work, literally translated into “working water”.
He developed a system in which plants grew through a perforated support from which the roots absorbed a nutrient solution contained within.
This technique is also used in the military field to supply the troops with vegetables during the Second World War. Today in the Netherlands more than 90% of greenhouse vegetables are produced with the hydroponic cultivation technique, the same is also used for the production of cut flowers. In recent years the need to reduce production costs and improve product quality, reducing emissions so that hydroponic cultivation has a positive feedback.
Hydroponic cultivation systems
Hydroponic systems can be classified according to:
- Presence and type of substrate (substrate cultures or hydroculture)
- Irrigation method (Drip irrigation or sub irrigation)
- Use of drained nutrient solution (open closed loop)
Substrate crops
Generally this type of cultivation is used for vegetables and cut flowers.
The plants in this case grow in containers of different shapes and sizes filled with inorganic or organic substrate. Using drip irrigation, nutrients are supplied 10 to 12 times a day. The system can be of two types, open or closed.
In the first case, the nutrient solution is drained and not used again; on the contrary in closed systems, where the nutrient solution is corrected and put back into circulation.
The choice of substrate, regardless of the economic side, must have some important characteristics:
Mechanical characteristics suitable for implant stability, high porosity (not less than 75-80%); suitable for reaction (oxygen) and water to ensure good water tightness and facilitate the gaseous exchanges of the plant.
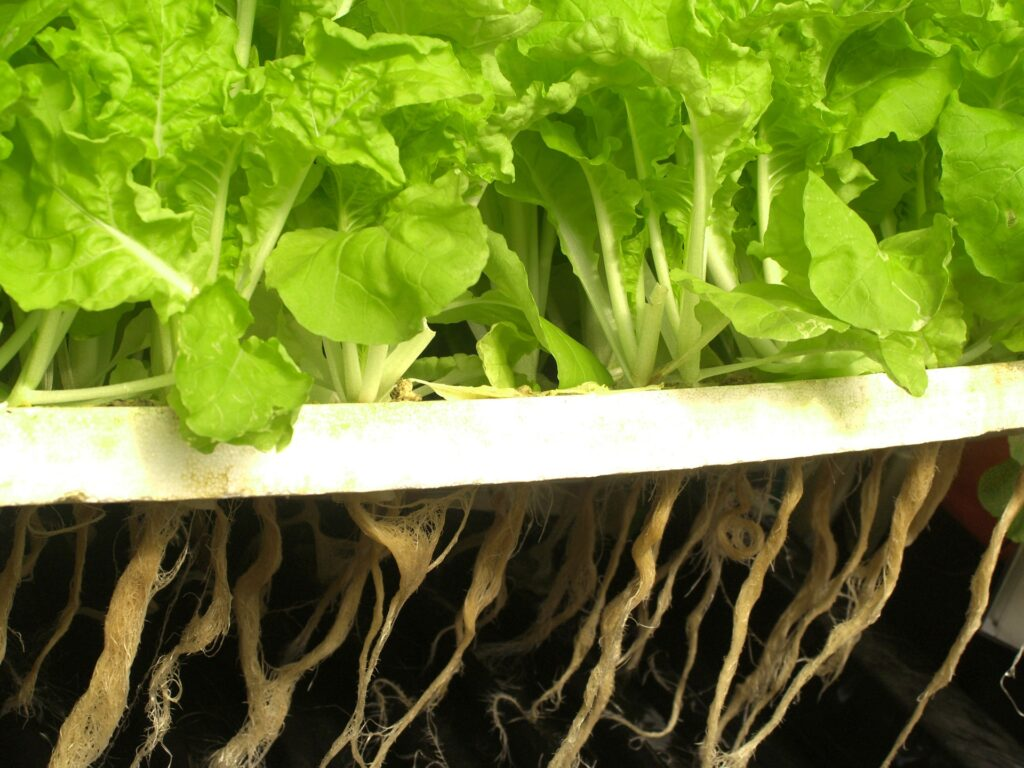

Composition of the nutrient
The nutrient used for hydroponics contains numerous nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, magnesium, and sulfur.
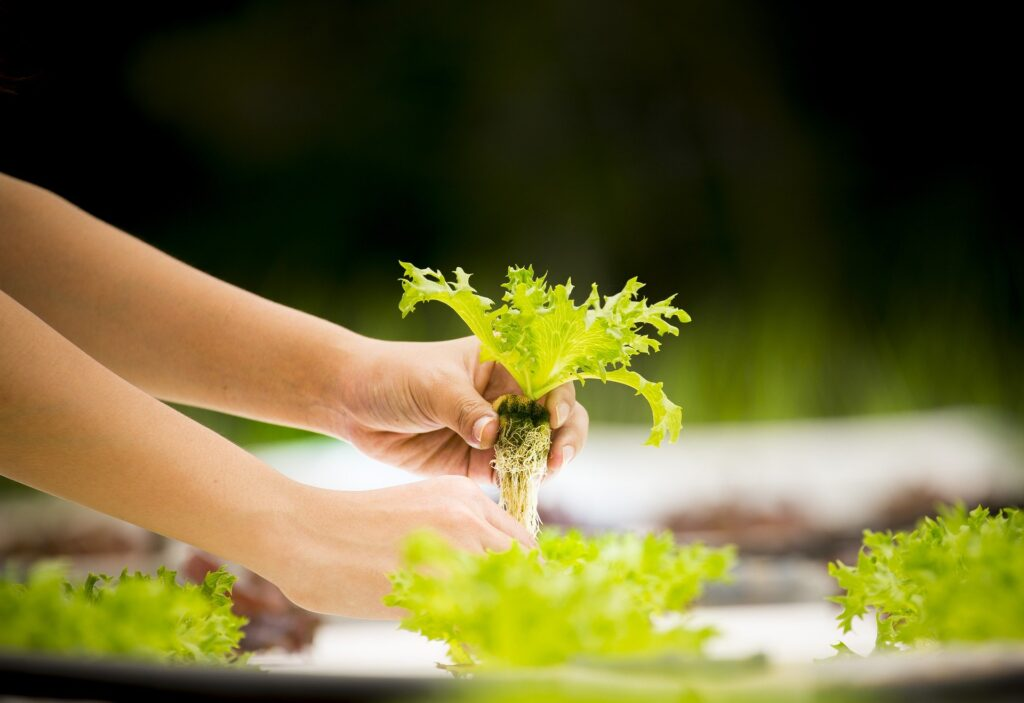

Hydroculture
For cultivation techniques in water, the most used are Nutrient Film Technique (NFT), the floating system and aeroponics.
Nutrient Film Technique (NFT) is a thin film of nutrient solution supplied continuously or at intervals, through sloping plastic channels in which the root system can grow. This is a closed loop system, the nutrient solution is introduced into the highest part of the channel and arrives by gravity towards the collection pipes.
Floating system the plants are placed on floating systems placed in trays filled with nutrient solutions. The system is mostly used for growing leafy vegetables and tobacco seedlings.
Aeroponic cultivation is a cultivation where the plants are grown in perforated plastic panels with the roots suspended in the air under the panel and in the dark to avoid algae formation. The roots are sprayed with a nutrient by nebulization generally every 5-10 minutes.
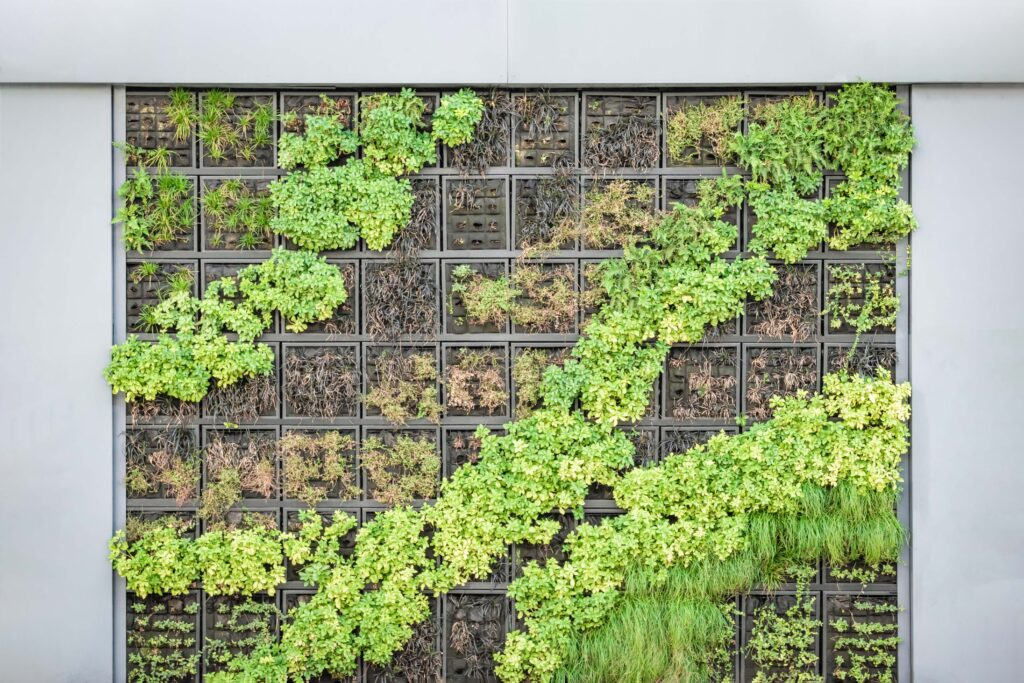

Construction of a hydroponic garden
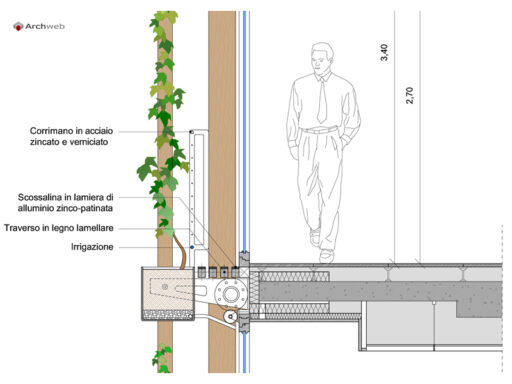
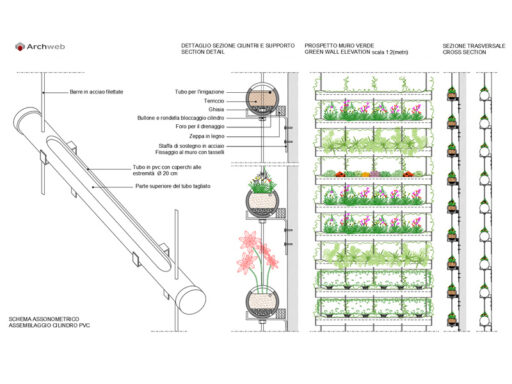
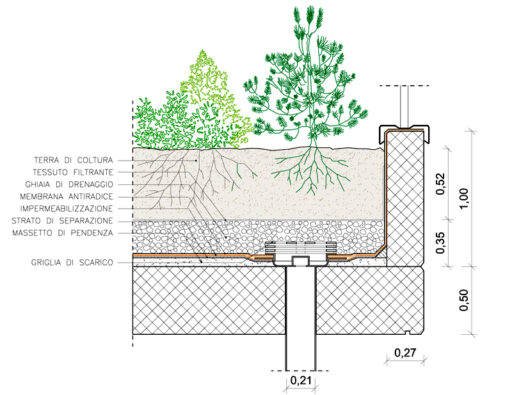
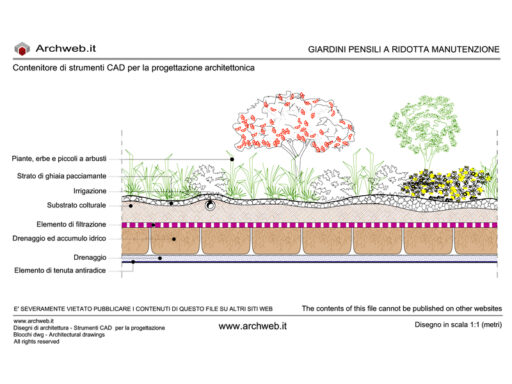
The hydroponic cultivation technique can also be used for aesthetic and functional purposes as in addition to the variable aspect that allows us to exploit the types of plants to create vegetable walls such as Patrick Blanc both outside and inside buildings, rather than to use it as partitions or sound absorbing walls.
On this topic, I invite you to also read: VERTICAL SURFACES: modern treillage

Bibliography
Tognoni, Franco & Malorgio, Fernando & Incrocci, Luca & Carmassi, Giulia & Massa, Daniele & Pardossi, Alberto. (2005). Tecniche Idroponiche per colture in serra. ResearchGate Jensen, M. H., 1997. Hydroponics. HortSci. 32: 1018-1020
Resh, H. M., 2001. Hydroponic food production: a definitive guide book of soilless food-growing methods. Woodbridge Press, Beaverton: 527 pp
Cover image: iamareri from Pixabay
© Archweb.com reserved reproduction – It is possible to share with a link to the page